Value Investing
What is Value Investing?
Let me try to explain this fancy, much talked about concept “Value Investing” by using the reference of the definition of Investopedia.
Value investing is an investment strategy that involves picking stocks that appear to be trading for less than their intrinsic or book value.
Value Investors believe the market overreacts to good and bad news, resulting in stock price movements that do not correspond to a company's long-term fundamentals. The overreaction offers an opportunity to profit by buying stocks at discounted prices.
Yes, value investing is indeed a strategy of identifying stocks whose current prices do not reflect their true worth. And when we say that we want to identify stocks at discounted prices, the question here is “by how much?” and that’s when we need to look at the crucial element of Margin of Safety.
Margin of Safety is the difference between intrinsic or true value of a stock and its market price. If we buy stocks with a slim Margin of Safety, it does not give us enough tolerance for error. If our judgement turns out wrong or if there is a sudden change in the planned events, we could end up losing a lot of our money. Hence, there must be significant difference in the price that we are paying or willing to pay for a stock and the price that we expect the stock to reach by the end of our investment horizon.
Investment horizon is another aspect of Value Investing that we need to be cognizant of. If you are a value investor, your investment horizon needs to be long during which any sort of short-term losses should have no bearing on your investment choices. A long-term view typically ranges between 1-3 years and beyond.
Now, it is not very difficult to understand that if you wish to be Christopher Columbus of the stock market wherein you identify stocks that the market has been unable to discover the true potential of, you need to spend a significant amount of time in doing your research in order to avoid herd mentality and make informed decisions. Value Investing is a very effort intensive strategy which requires you to not only do quantitative analysis of financials but also qualitative analysis of management practices, corporate governance, scope of growth in the business and industry, et cetera.

Pictorially, we can say that Value Investing is the triangle at the centre where the 3 circles meet. ALL THREE elements of the holy trinity of value investing are essential for any investment to qualify as good value.
I. Lack of growth opportunity limits upside due to lack of high potential earnings in the future. Even if a company has solid financials today, the lack of reinvestments in the business owing to a saturated or mature industry will mean a very slim Margin of Safety which is unadvisable.
II. Any business with poor quality corporate governance can never generate sustained high returns because of lack of reliability. Scope for growth and plans of growing is only as good as its actual execution.
III. Sound financials is a direct reflection on the company’s current operations and reputation. Even the best practices of an industry may not be the ideal choice of action for the particular business. Every business is unique and requires a customized strategy in operations.
The Golden Rules of Investing
Now that we have a brief idea about value investing. Let us discuss the Golden rules of value investing.
“An important key to investing is to remember that stocks are not lottery tickets” - Peter Lynch
The stock market is a device of transferring money from the impatient to the patient. We have witnessed a lot of rags to riches stories in the stock market, but every story of a successful investor has one common factor which is Research. Today, we will understand the success mantra of one such successful investor (Mr Raamdeo Agrawal of Motilal Oswal Group) who is an Indian businessman, stock market investor and joint managing director of a financial firm having a market capitalization of more than ₹8800 crore, known for his focus on value investing.
There are four major pillars of any successful value investing strategy:

We will discuss each of them in subsequent units.
Power of Focus
First with the ‘Power of Focus’
“Price is what you pay, Value is what you get”- by Warren Buffett
The prime focus for an investor is to get the maximum value out of the investment that he makes. Value investing helps chase the change in value of the investment, that is, the delta. The market is continuously pricing the stocks according to its knowledge and hence it is very important for an investor to get ahead of the market.
To get ahead of the market, an investor should focus on some specific good companies, do in-depth research on them, and apply value investing based on past data.. Past data is a reliable source to select these few good quality companies. Value and not the price of the stock should be taken into consideration while selecting your focus companies.
Our veteran investor’s mantra in life is to “Buy companies that are rock solid from the inside”. He says that if a company is broken and is not making money, no matter who is buying that company, he will not buy it. This is a big lesson in life. We all tend to become victims of herd mentality. We hear of someone who has a great track record and has made a lot of money in the stock market in the past and we then try to follow their footsteps. It is okay, even advisable to follow what they are doing because that can narrow down the process of identification of good stocks but SELECTION of investment choices should only come from one’s own research and faith.
The power of focus entails predictability. In value investing, a company which has done very well in the last 3 years but was bad for 8 years should be avoided UNLESS there is a strong belief that the company is turning around after having made noticeable changes in their operations, management, etcetera. Without solid evidence that there is scope of turnaround, such an unpredictable company must be avoided.
Focusing on quality companies requires you to analyse key financial ratios such as Return on Equity or Return on Capital Employed, identify unique selling propositions, thoroughly read the Director’s Report and Management Discussion and Analysis (MD&A), look for sizeable opportunity in the industry and also perform SWOT & Porter’s 5 Forces analysis to understand of external factors affecting the company and its performance.
Power of Price
Second, the ‘Power of Price’
We mentioned how it is the value that needs to be looked at when “selecting” future companies. That does not mean that price is to be disregarded. It is just that value needs to be looked at FIRST and then price.
So, what is the difference between the two?
Value is something invisible that is derived from the business and the story of the company. However, price is the value that the market assigns to that business.
It is important to know that good stocks do not always rally upwards. A good stock will drop when an irrational investor exits. That is when the rational investor needs to sit back and hold. In value investing, you must hold a stock when you believe in the attractiveness of the business, rather than being swayed by the price movements.
It is imperative to analyse if the investment has the potential to provide expected returns in the intended time horizon. Let me introduce you to the Rule of 72 here which will help you to roughly calculate the time span in which your investment will be doubled. If a stock’s compounded annual growth rate is 40%. Then your investment in the stock will double in = (72/40) years i.e. 1.8 years.
[Formula: Years to double = 72/growth rate in percentage]
Now, suppose the P/E of a particular stock is 60 right now and its earnings are expected to grow at a CAGR of 40%. Let the current price of the stock be P1 and earnings per share be E1. Therefore, P1/E1= 60. Five years later, let the earnings per share be E2. As the earnings grow by 40% each year for 5 years, E2= E1*(1+40%)^5
(1+40%)^5 = 1.4^5 = 5.38= 5 (approx)
Therefore, E2= 5*E1
So, 5 years later, if the price of the stock remains same, i.e. E1, the P/E ratio becomes P/E = P1/E2 = P1/5*E1 = 60/5 = 12
When estimating future earnings growth, another important thing to keep in mind is to estimate how much of this future growth is already discounted into the current price. For this, it is important to understand what all does the market overtly know. To beat the market, one needs to conduct in-depth analysis which can uncover a lot of hidden information about the company (both qualitative and quantitative). This information will not be factored into the current price and that gives the opportunity to a rational, well-researched value investing approach to make money in the stock market.
Power of Quality
Third, the ‘Power of Quality’
It is not sufficient to buy stocks just on the basis of favourable price but one should also look at Quality Growth Longevity as the key to Value Investing is “Buy Right, Sit Tight”.
Every business is a capital input-output machine but a terrific business will not always require an investment of 1000 crores to earn 1000 crores. It can be achieved with less investment but with a brilliant management exhibiting terrific corporate governance. Today, there is abundant hunger in management all around us in terms of competitiveness and the drive to strive for excellence. What sets one management team apart from another is integrity. That being said, having a good business is non-negotiable because it is futile to have a great management but one which is unable to assert their greatness into the business, a core principle in value investing.
In reality, it is actually possible to earn money from any company in the short run if one time their investment has been done correctly, however, astronomical returns can only be achieved with quality companies. Quality businesses are businesses which consistently earn above their cost of capital irrespective of the business cycle, but they do not come cheap and hence it is again about identifying these companies before the market does. In true essence, Power of Timing supersedes these 4 golden rules.
Moving a step forward, we can try to quantify the term“quality” using the following parameters:-
- RoE & RoCE: Return on Equity (RoE), Return on Capital Employed (RoCE) should be at least 5% above risk-free rate (10 year bond yield)(The current 10 year bond yield is about 6.1% (Feb 2021)). That puts the benchmark rate at about 11% which implies that a business must earn this RoE or RoCE every year for a minimum of 5 to 10 years.
- Favourable Terms of Trade: A company should have a fast sustainable collection period i.e. shorter debtor days and longer payment cycle i.e. longer creditor days. The word “sustainable” here is as important as “fast” when talking about the collection period. This is because having a consistent period of debtor days shows that the company shares a good relationship with its customers.
- Operating Cash Flow & Free Cash Flow: One of my professors once quoted, “There are only two certainties in life and they are cash and death”. This saying is corroborated with the emphasis that our veteran investor puts on cash flows. Profits can be manipulated and tampered with, however, cash will always give you a true picture of the strengths and weaknesses of a business in the context of value investing.
- Growth & Longevity of Growth: It is not just important that the company grows with a high rate but also that there is scope of growth in the industry. To understand growth rate, one doesn’t need to look at a company’s current position (say, market share) but its future potential. A company with a 2% market share but very competitively advantaged with a strong moat can grow to 20% in a short span of time and that’s quintessential wealth creation. In value investing, Moat is a term which is commonly used by Warren Buffet to describe a company’s competitive advantage that acts as a barrier for entry for another firm who wishes to enter the same or similar type of business. There are various sources by which a company can set up its moat, namely, cost advantage culminating into high margins, efficiency in production, high switching costs for both employees and customers, network effects in the form of a strong customer base, patents and regulatory licenses, strong brand image, etc.
Power of Compounding
The last is the most important one, i.e. the ‘Power of Compounding’
Let us explain this concept with the help of an example.
The table below shows what ₹1000 invested for n=10,20,30 years will be if invested at a rate r=4%,6%,8%,15% respectively.
The formula for compounding is : FV = PV (1+r)n
Here, FV = Future Value, PV = Present Value, r= rate of investment, n=investment horizon (no. of years)

Table: Power of Compounding
Value Investing is investing money for the long term and when we take equities, the CAGR of the equity market for the last 10 years has been around 13.6% (according to global investment bank, Goldman Sachs).
Moving forward, what everyone should be aware of is that financial planning requires you to understand that inflation dilutes the value of money and thus, act accordingly. For a very rich guy, all you need to do is preserve your purchasing power which can be as simple as investing in safe government instruments. However, for the middle working class like myself, we need to invest in a way that not only beats inflation but also gives us more purchasing power through strategies like value investing.
Hence, we need to comprehend the knowledge of compounding and apply it in our investing style. It is a friend of good companies and a foe of bad ones.
“Compound interest is the eighth wonder of the world. He who understands it, earns it … he who doesn't … pays it.” - by Albert Einstein.
Techniques of Value Investing
Earlier, we learned the golden rules of value investing based on which let us discuss a few techniques of value investing.
Value Investing is an arduous task that requires substantial efforts to be put in analysis of a company and its industry. The fundamentals of value investing are not complicated and can be employed by even unsophisticated investors to identify stocks that are a good buy and have a potential to generate substantial returns in the future. Some of these basic principles were identified by Benjamin Graham in his book ‘The Intelligent Investor’ back in the mid-1990s and several of these are relevant even in today’s time.
One of the key concepts introduced by Graham is the intrinsic value of a company or its stock. Intrinsic value in plain terms is the true value of a stock. The basic tenet of value investing is to determine this intrinsic value for a stock and then buy those that are trading at prices below their intrinsic value. By thorough analysis of the financials and business of a company, a value investor aims to uncover stocks that are undervalued with the belief that the market will eventually realise its value at a later point of time and the price will correct to a higher level.
Value investing entails several more criteria than the frequently recited phrase “Buy stocks that have a Price/Book-Value (P/B) ratio of less than 1”. It is important to club this factor with several other criteria to determine stocks that are not only cheap but are also backed by a financially sound company with a strong business model. P/B ratio below 1 can very well correspond to a company that is financially weak and on the verge of failure. This is why an exhaustive analysis across multiple aspects is essential to get a holistic picture of the actual value of the company. There are also situations where certain criteria work better than others. E.g. P/B ratio is more relevant when analysing companies that are capital intensive but tends to be less effective in case of non-capital-intensive firms.
Rather than looking at the absolute values of certain ratios, comparing these ratios for a company to the ratios for similar companies in the industry often yields better results. This is especially relevant in the case of valuation ratios such as Price/Earnings (P/E), Enterprise Value / EBITDA (EV/EBITDA) and Price to Book value (P/B).
Another metric that Graham considered as one of the more accurate representations of a company’s worth was Net Current Asset Value (NCAV). It is a rough measure of the liquidation value of a company. A company’s liquidation value is estimated by subtracting the cash owed to the firm’s creditors from the cash that could be received if all the hard assets of the firm (excluding intangible assets) were sold and the business was closed.
The technical formula for NCAV is:
NCAV = Current Asset – Total Liabilities – Preferred Stock
where, Current Assets = Debtors + Inventory + Cash & Cash Equivalents
Total Liabilities = Current Liabilities (Creditors) + Long term borrowings
Companies whose NCAV per share (NCAVPS) is below its share price can be used as one of the criteria to identify companies that are a good buy from the perspective of value investing.
A downside of using such a measure is that these criteria are relatively skewed towards identifying companies that have been colloquially termed as cigarette butts. These are beaten down companies that are trading below their value of liquidation. While getting a share at a substantial discount to liquidation value might give decent returns in the short term, it is not a useful strategy of value investing from a long-term perspective. In a few cases, these cigarette butts might be firms that are real gems and have a strong revival potential.
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Valuation
There are alternative methods to get an idea of the intrinsic value of a stock apart from those suggested by Ben Graham. One of the most popular methodologies is DCF Valuation. The full form of DCF is Discounted Cash Flow.
The formulae that we need to know to perform Discounted Cash Flow or DCF calculations are as follows:

FCFF = NOPAT + D&A – Capex – Change in Net Working Capital
NOPAT (Net Operating Profit after Tax) = EBIT x (1-t)
Terminal Value = {FCFn x (1+g)}/(WACC – g)
Now, let us explain the concept of DCF using the example of a company listed on the stock exchange:




Value of Time Warner (Total of PVCF) = $9924.14 million or $99.24 billion
Now, we calculate the per share value of Time Warner and compare it with the market price at which a single Time Warner share is trading in the stock market.
Say, No. of outstanding shares = 10,000 million
Market price of Time Warner = $100
Then, Value per share (refers to Intrinsic or true value here) = $99242.14/10,000 = $99.24
Discover the secrets of value investing in our 'Stock Investing Made Easy' course. Enroll now and unlock your path to financial success!
Since true value is lesser than the current market price, the share is said to be overvalued. It is expected that in some time, the irrational investors will exit the market and the price will converge to its true value, thus falling down to $99.24. Thus, if we sell the share at $100, we will be making a profit when the stock falls down to its true value.
Relative Valuation
In continuation with the explanation of the Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) method and DCF calculation from the last section. Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Valuation is an absolute value model that aims to determine the intrinsic value of a stock on the basis of the present value of the company's expected future cash flows. While it is a fundamentally sound technique to value investing in a stock, it falls short on the parameter of practical relevance. Stock market prices are very often driven by macroeconomic factors and market sentiments rather than just the company fundamentals. These factors that affect the entire industry and stock market are not taken into account in DCF Valuation. This is where Relative Valuation comes into picture.
Relative Valuation, specifically Comparable Company Analysis is a business valuation method that compares a company's value to that of its peers in the industry in order to assess its financial worth. In times of stock market crash or rally, the prices of a stock are completely disjoint from their fundamentally derived intrinsic value. Even in such cases, relative valuation gives us a method to compare a stock of a particular industry to its competitors and determine if it is a good buy or not. Some commonly used ratios are Price to Earnings (P/E), Price to Book Value (P/BV), Price to Sales (P/S). Out of these three ratios, it is not advisable to use the ratio P/S as the comparison between Price and Sales is incorrect. This is because the market price of a stock captures the equity or shareholder part of the wealth of the firm whereas sales captures both the equity and debt component of the stock. A ratio should be consistent for it to be accurate and reliable.
An important prerequisite for carrying out relative valuation is that the companies being compared should not only belong to the same industry but also have similar underlying business model. Just like it's not possible to compare apples to oranges, companies whose business models are different cannot be compared. For example, comparing SBI cards to ICICI Bank would not be an appropriate comparison even though both companies are financial services companies. SBI Cards is a pure play credit card company while ICICI Bank is bank making their business models completely different. In value investing, comparing ICICI Bank to a company like HDFC is an appropriate comparison.
Another type of relative valuation method is Precedent Transaction Analysis where, historical transactions determine the current value of a company. Most commonly, these transactions fall under the category of Mergers and Acquisitions as it shows what another investor was willing to pay for the entire company. Certain ratios may also be used such as EV/EBITDA.
Five Common Misconceptions of Value Investing
Till now, in this module, we have explained the concept of value investing in complete detail. In this unit, let us discuss some common misconceptions of value investing.
1. Investing in Blue-Chips: First, let us define stocks which are labeled as Blue-Chips. Huge companies, essentially those with a >$5 billion market capitalisation and excellent reputation are commonly called blue-chip stocks.
In simpler words, they are safe equity investments having been termed as “safe” due to their long history of generating dependable earnings (profits for the business) and having established trust due to their sheer scale.
It is a common misconception that investing in blue-chip stocks is a means of practicing value investing. While blue-chip companies are usually more resilient to both internal and external disturbances due to their sheer size and governance practices, they might often turn out to be companies that are highly overvalued.
The basic tenet of value investing is that the current price of the investment represents a good value from the perspective of current and future earnings and potential growth. Blue-chip stocks represent a safer investment as compared to other companies of smaller sizes but a company belonging to the latter category and backed by a strong business might represent better value.
The history of the financial markets is replete with instances when mid-caps and small caps have outperformed large cap companies. One such instance is shown in the below graph where the Nifty mid-cap 100 index generated a return of 50.4% whereas Nifty 50 gave returns of 30.95%. as on Nov 2021
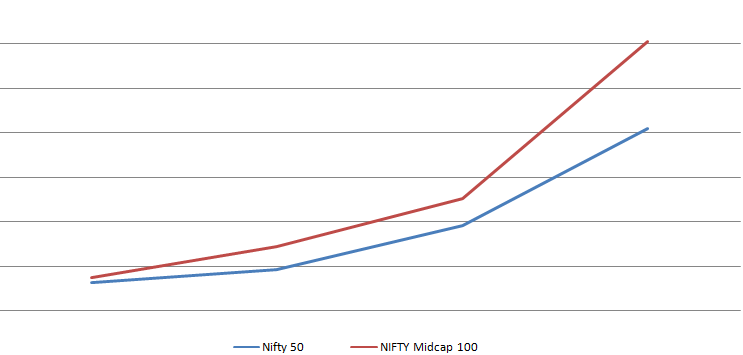
At the end of the day, the motive of most investors is not just to minimize risk but get highest possible returns for the quantum of risk being taken. It is also a rarity for large cap companies to turn into multi-baggers. Blue-chip companies are closely tracked by a large segment of market participants and hence every development, whether positive or negative, is reflected in the price within a very short period. Smaller companies are not tracked as exhaustively by analysts and other market participants which gives opportunity for an investor who recognizes a strong company with a sound business model early to realize higher returns.
2. Keeping up with the trend: You often hear people chasing stocks giving monumental returns for some short period of time. These may very well be the same stocks that give you monumental losses in another time period. In technical terms, these stocks could either be cyclical stocks or they could just be those stocks which are riding the bull market at the time when the entire market is up and investor sentiment in general is very high.
If they belong to the latter category and are incapable of generating returns based on the worth of their business, you need to steer clear of them for long term investing. Moreover, most often than not by the time these trending stocks become visible to the minority shareholder, it is already too late to make hay while the sun shines even for short term gains.
On the other hand, if they belong to the cyclical industry, you can very well invest in them provided you fully understand the industry and can identify the correct entry and exit points. This not only requires you to invest a lot of time in keeping up with day-to-day news but also requires a fair deal of technical knowledge of not only the industry but its external environment as well.
Hence, keeping up with the trend wherein you just invest in stocks “currently” delivering high returns is not always the best approach from a value investing perspective.
3. Diversificatio: Time and again, we have been taught “diversify your portfolio” and “hedge your business risk”.
What does this really mean? Are you supposed to hold 100-200 stocks of different industries?
Well, I am of the opinion that ‘Too many cooks spoil the broth’ because it is nearly impossible to hold 100 stocks which are all of substantial quality. So invariably, you will have a lot of junk stocks which aren’t reliable to generate good returns in tough times. Hence, it is better to limit your portfolio to a maximum of 15 stocks because:
a. It is easier to keep track of a smaller number of stocks, whether it is business performance or corporate governance and hence avoid keeping any junk stocks in your portfolio.
b. 15 is a good enough number to achieve optimum diversification whether it is across industries, geographies, value chain, et cetera.
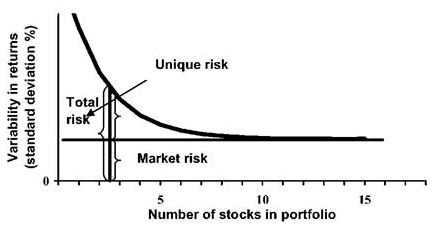
Source: www.ebrary.net
Total portfolio risk as a function of the number of stocks held (%)
As we can see from the figure above, the incremental diversification after holding 15 or more stocks is minimal. This is where you have to take into account other factors such as transaction costs which increase significantly with the increase in the number of stocks. Moreover, as we know, diversification can only be achieved for “unsystematic or business risk” and adding more stocks will not be able to mitigate “systematic or market risk”. Hence, it is never really possible to hold a portfolio of equity investments without bearing some significant risk.
4. Never losing money if you follow the ideal steps of Value Investing: An interesting article that I came across recently tried to draw parallels between a game of poker and the game of investing.
Having played Poker for more than 6-7 odd years, I consider myself to be decent enough when it comes to understanding the intricacies of the game. However, there have been several times when I have lost a lot of money even after having a great hand. Now, there are two reasons that my loss can be attributed to:
Either ‘Luck’ or, ‘Being unable to gauge competition’.
Now for both the above reasons, the article gave me some invaluable advice that I’d like to share with you.
I. “On any given day, a good investor or a good poker player can lose money” – David Einhorn
We must always remember that investing is a probabilistic exercise and even following the ideal steps of value investing DOES NOT guarantee you profits or promise you zero losses.
II. “Life is like a poker game where you must learn to quit sometimes when holding a much loved hand.” – Charlie Munger
It is imperative that you gauge the odds of the competitor winning in poker and not let your biases of a good hand prevent you from folding. Similarly, in value investing, it doesn’t matter how flawlessly the business is being run if it’s the wrong business (say likely to be disrupted by technology) or if it’s in too small a market (showing no scope for major growth). Looking at the bigger picture is absolutely essential in order to prevent encountering losses in the long term.
5. Know every detail about the business and company: Understanding the industry, business and company well is not the same as knowing every last detail about the three.
“A company should be viewed as an unfolding movie, not as a still photograph” – Warren Buffett
Continuing with our comparison with a poker game, we must understand that with every card, we get to know more but we never really fully know everything until the last card. However, we cannot wait until the last card to raise our bets. We have to play the game based on the probability of a hunch we had in the beginning of the game and by continuously taking into account the forthcoming developments.
Similarly, spending a lot of time to discover the last unanswered detail may cost us the chance to buy a stock at a favourable price. As we know, greater the uncertainty, greater the potential returns from a well-timed investment. Hence, acting quick is a necessity in the game of value investing where things change with the blink of an eye. That being said, it is about taking smart calculative chances and not just gambling our money away. Having a reasonable knowledge about the company and business should be a good enough reason to go ahead and invest in the same.
Note: Now that we have completed our module and discussed all the concepts of value investing, let us indulge with some case studies in the subsequent units.
Case 1: Relaxo
Case 1: Relaxo (by Ravi Purohit, CIO of Securities Investment Management Pvt Ltd.)
This is a case study from 2013 when Mr Purohit’s firm was still invested in Relaxo and its future potential was being analysed.
Facts
- In 2013, Relaxo’s strategy was to use iconic brand ambassadors with the likes of Mr Salman Khan, Mr Akshay Kumar and Ms Katrina Kaif.
- Very high Advertisement and Sales Promotion expenses, almost to the tune of ₹144cr when pre-tax profit was a mere ₹67cr
- Pre-tax Return on Equity (RoE) was 35% in 2012 vis-a-vis 14% 10 years back.
- Company pays low dividends
- Average realisation per pair was RS 100 (or less than $2). A US company, Havaianas sold high end flip flops for $90.
- In the FY 2013, the company sold 100 million pairs of footwear having grown from 64 million in 2008. Profit per pair was a meagre ₹4.48 having grown from ₹1.64 in 2008.
Learnings
1. This case study helps us understand branding and heavy advertising in a big way. The sole objective of heavy advertisement and marketing campaigning should not be visibility. That’s the preliminary objective to get the brand to enter a consumer’s Awareness Set. However, the final and most important objective is culminating that awareness into purchase and hence, profitability for the company. The lesson learnt here is that it is not sufficient to heavily advertise just so that the consumers know about the brand but the marketing pull should be so massive that the consumers actually purchase the brand’s products and continue purchasing in future as well, , just as value investing focuses not only on identifying undervalued assets but on long-term returns.
2. One should not look at any line item on a standalone basis. A high advertisement expense with relatively low profits does not mean that the expense is not justified. There is a lot of subjectivity involved in accounting. In Relaxo’s case, it would have been better to have capitalised the advertisement expense and then amortized the same over a given number of years.
One should capitalise an expense when the benefits of that expense is of an enduring nature, in the sense that it leads to long-term benefits. To prevent accountants to inflate profits by this accounting gimmick, one must perform two tests for an expense which is being capitalised. It should be checked that the RoE (Return on Equity) before the treatment is high and secondly, the company is gaining and not just maintaining market share. Any expense incurred to maintain market share is of a defensive nature as not incurring that expense will lead to a loss. That means, spending that money won’t take you forward in your growth trajectory but will only enable you to stay where you are.
3. The company should have a vision in mind of where it wants to go. Havaianas was Relaxo’s goal and that’s where it was heading. This helps the investors understand the opportunity of growth of a company.
4. Low dividends doesn’t mean that the company is unreliable. What needs to be checked is whether the company is generating money and if it is, then what is it doing with that retained money? If the company is able to reinvest that money into the business to generate greater profits, why should one complain about low dividends?
5. A company with a moat has a reliable and investment-worthy business. Having explained the concept of moat before, we see that Relaxo’s moat has its cost advantage, high volumes and production efficiency. Selling a pair of slippers for less than ₹100 and making a profit of just ₹5 per pair was not a replicable business model. A competitor would need significant investment to achieve this level of economies of scale and also, they would have to sustain negative margins for a long time if they wish to take market share from Relaxo. Negative margins would be on account of heavy branding expenses, low price of footwear, high raw material cost on account of being a new player, et cetera.
6. The company’s cost advantage enabled it to price its footwear really low but didn’t ensure high margins. However, sometimes low margins work in your favour because not only does it keep competitors away (due to lack of attractiveness of such a business model) but also leads to a sustainable business model where customers’ loyalty to the brand keeps on growing (can be corroborated by company’s turnover ratios).
7. When investing for the long term, one must ensure that a business is good today and will be good tomorrow as well. In simpler words, the business should not become obsolete. Relaxo’s business model is of an enduring nature and not prone to rapid change either. In Buffett’s words, “A moat that must be continuously rebuilt will eventually be no moat at all”
Case 2: Safari Industries
Case 2: Safari Industries (Thesis by Sumeet Nagar, Managing Director of Malabar Investments)
Mr. Sumeet Nagar managed a fund size of ₹830 crores in March 2018 when he explained his thesis of investing in Safari Industries at the time.
Mr. Nagar’s Funda of Value Investing:
I. Quality of Business: The business can earn a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20-25% only if it has a moat. The company need not require outside capital to do so either if they have a strong business.
II. Quality of Management: The management must exhibit the following-
a.Operational capability where they not only know the business well but also the industry and competitors
b.Capital allocation discipline
c.Integrity
These two parameters are used as a basic filter to identify good companies by Mr Nagar. Now, in the case of Safari Industries, he explains that it was not a traditional pick for him. He usually invested in market leaders who are No. 1 in what they do. However, Safari Industries was at No. 3 after VIP Industries and Samsonite but that meant that there was greater value to uncover and beat the market.
From 2002 to 2012, the sales of Safari Industries didn’t grow but after that they got a new management who was the former MD of VIP Industries.
This was a major green flag for Mr Nagar and that’s when he started closely watching the business movements. The sales of the company grew at an annualised rate of 30% for 5 years after 2012.
Moreover, there was a significant opportunity available in the industry. It was an industry of branded players where, 90% market share was of branded business. He also applied Second Order Thinking to analyse the growth potential in the industry. He connected the growth in the aviation industry and two-wheeler market with the growth potential for the backpack industry.
Learnings: It is important to look at factors likely to impact a business from all domains. At times, macro factors tend to be more important than just micro ones. Connecting things which are less obvious to the general market is what can make an investor a successful one.
Conclusion:
So, from this module, we have completely understood the art of value investing. This is the way through which investment gurus like Warren Buffett and Peter Lynch have earned billions. It is time for you to get started with your investment journey. We also have more modules on ELM School, which you can go through for a better understanding of overall financial markets, investing and so on.


