Introduction
‘Success is the residue of planning’- by Benjamin Franklin.
The above quote shows the importance of planning in achieving success in each task. Similarly financial planning is important to achieve our financial goals.
In this module, we will learn about financial planning and its importance. Not only that, we will discuss how to plan for each stage of our life and become financially independent. So, without any further ado, let us start:
What is Financial Planning and Why do we Need it?
An earning person is faced by different types of expenses in their daily lives.
Some may be expected and accounted for - rent, school/college fees, or household expenses - whereas some may be completely unexpected, like expenses for a medical emergency.
Along with such expenses, we will have to start saving money for our retirement as well.
It would be perfect if we could set out a way to handle all these obligations and expenses while maintaining good standards of living.
Unfortunately, two circumstances prevent this from happening -
i. Inflation
Something that costs you ₹100 today, could cost you ₹110 tomorrow. Let us discuss an example to bring out the point.
Suppose a situation in which, your monthly household expenses = ₹30,000;
Years to Retirement = 15;
Inflation Rate = 8% p.a.
Therefore,
The household expenses you will have to incur at the time of retirement to maintain the same lifestyle = ₹95,165 per month.
ii. Improper Investment of Money
The lack of proper research and planning before making our investments can kill the benefits its future value can give us.
To prevent these circumstances from harming our financial well-being, we need a proper road-map of how to spend and save money.
This process of developing a plan of spending and saving in such a way that we can maintain our standards of living while covering our expenses is 'financial planning'.
The process of financial planning involves -
1. Determining our risk-profile
2. Quantifying our goals
3. Tracking our incomes and expenses
4. Setting our goals
5. Monitoring our progress towards our goals
The process of financial planning is important for us to follow because it helps us manage our needs and wants.
While needs are things we cannot live without, wants are simply objects we wish to acquire in the future.
Financial planning helps us manage both of them efficiently, while making sure our standards of living are maintained.
Financial Position
Financial Planning starts with evaluating our current financial position. Let us know how:
What is your financial position today?
The very first step in financial planning is to understand where we stand from a financial point of view.
We can understand this by measuring our financial health.
Just like a human requires regular checkups to make sure their health is well, you need to constantly measure and check up on your finances to make sure that they’re doing well too.
You can use the following formulas to determine your financial health -
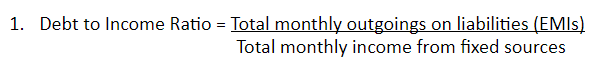
Ideally, your debt to income ratio should not be higher than 30%, as this would mean that you are straining your income.
This means you should not be spending more than 30% of your income on paying loans / interest on loans.
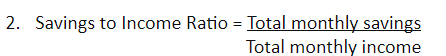
Ideally, you should be saving at least 20% of your monthly income to save and invest.
Contingency Reserve = 6 to 24 months of your living expenses.
You should set aside 6 to 24 months of living expenses as a contingency fund to be used only in times of emergencies. This should include any EMIs that you may have.
After implementing these simple rules, you will find that your finances are more in your control and manageable.
How to Build a Contingency Fund
Generally, everyone experiences various demands or requirements at certain stages, like children’s education, marriage or retirement.
But, the one need that is constant at any stage is the need for liquidity.
In simple terms, it is the need for ready cash, which may arise for an emergency like medical attention and expenses.
Hence it is imperative that we take this requirement very seriously and build enough cushions to face any eventuality at any time.
These cushions include contingency funds.
The thumb rule is that one must have at least 3 to 6 months of gross income available during an emergency.
This time limit can also depending on other factors like -
- The number of dependents, especially considering whether they are older or younger dependents; and
- The number of earning members in a family; etc.
The fundamental factors that have to be considered for building this cash cushion are:
- Money should be available at call.
- There should not be any conversion cost – to convert the investments into cash.
- The income should be taxed only on withdrawals, and not on accrual basis.
Emergency Funds
Previously we have learned how creating a contingency fund, or an emergency fund is an essential step in financial planning. Now let us discuss the different investment options that will help build an emergency fund. These include -
Savings Accounts
This account is one of the most basic methods of building an emergency fund.
It should be ensured that the funds of this account should be used judiciously and it should be ensured that some money out of this fund can be used for investing in higher interest-bearing options.
Bank Deposits
These days, banks offer many different types of deposits to cater to our needs.
One of these include the flexi deposit, which has the following unique features -
- You can deposit whatever amount you want in the account. The minimum deposit is ₹500.
- You can even deposit money multiple times in a month but there will be a penalty for not depositing once in a month at least.
- The tenure for these accounts is relatively bigger - the deposit has to be operated for a minimum of 5 years.
Debt Mutual Funds
Apart from the safety net of extra income through interest, debt funds are known to be liquid as well.
Once redeemed, your proceeds can reach your bank account in 2-3 days.
While choosing a method of building a contingency fund, keep the following points in mind -
- Take tax incidence seriously:
As mentioned above, tax incidence should be viewed very seriously, when one selects any instruments for liquidity purposes.
- Don’t complicate investments made for liquidity purpose:
As per the amount one needs to save for this requirement will not be significant in relevance to once total savings, the investor should look at simple and minimum instruments.
- Don’t go overboard on liquid investments:
It is also necessary for one to calculate and freeze the requirements at some level, so that no one can keep more-than-necessary liquid instruments leading to opportunity cost losses, especially if the additional investments could have been directed into growth schemes having much better rates.
Let us consider a case to understand this concept better.
Pratik and Amrita Ray are a double income earner couple and have been setting aside money to create an emergency fund. Their goal is to have at least a year's expenses set aside for contingencies despite never having dipped into the funds they have accumulated so far. The Roys think it is wasteful to leave the funds in their bank account and wonder if they should invest and generate good returns. They want to know if this is the right approach to build an emergency corpus.
The primary purpose of a contingency fund is to help tide over any shortage of income or an emergency. As the couple's financial situation is secure enough, it gives it the leeway to consider investing a portion of these funds to earn a better return.
Following are the ways to go about this is to split the corpus and invest to ladder the risk :
- The Rays' must look at building a corpus which is equivalent to three months' expenses.
This should be invested in a secure and liquid product, such as a bank deposit, so that it can be easily withdrawn. - They can also look at investing an additional three months' funds in an instrument that gives better returns, such as a short-term debt fund or flexi deposits of banks, without compromising on liquidity.
- The last tranche of funds can be invested for higher returns by taking more risk. The investments that have a lock-in period should not be considered even if they give better returns since they defeat the essential need for liquidity.
One important feature that the Rays should consider while selecting a higher risk investment is their ability to offer them as security for a loan.
The blend of investments selected by the Rays' depend on their personal situation and risk profile.
As both of them earn, the stress due to loss of income will be lower. Similarly, if they have accumulated assets that can be redeemed in case of an emergency or loans that can be availed of, such as home equity, it will give them greater flexibility in investing their emergency fund. Any change in their situation will also imply a re-look at the way their contingency fund is invested so that its relevance is not lost.
Financial Habits
Now that we have set aside a major portion of our wealth for emergencies in the form of Contingency fund or Emergency fund. Let us discuss a few financial habits that everyone should follow in order to achieve any financial goals:
What are the financial habits, or the lack of them, that have brought us to our current level of financial health?
When you sit down to assess yourself, it is all really about only two things:
1. Are you living ‘within’ your means or 'below’ your means?
By this we mean, is your level of saving the level that you require, or do you save that little bit extra and – invest it?
2. What do you spend on and how much do you invest?
This means, is your expenditure primarily on luxuries or necessities? Accordingly, are you investing as much as you can or are you spending the cash that could have been invested instead?
These two important factors will determine whether you will be able to send your child to that excellent school, or buy the more beautiful house, drive the bigger car, take the longer vacations and retire those few years earlier. These are all financial goals. As we advance in this module, we will discuss the importance of financial goals and the steps to achieve them.
As of now, we have to focus on four important financial heads -
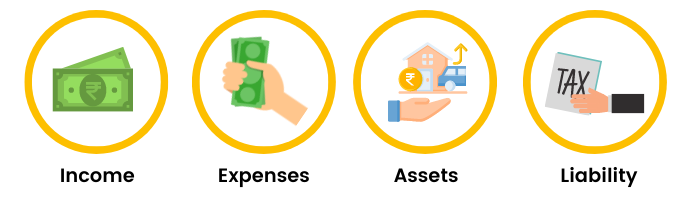
Money tends to flow between the above heads.
Our income will fund our expenses and will take care of the full or part purchase of any assets we may buy. Part purchase of assets can be supported by taking on liabilities. Our liability payments are in turn again funded by our income. Keeping track of this money flow is called budgeting. We will study the concept of budgeting and understand its necessity in the next section.
Budgeting
What is Budgeting and Why is it Necessary?
The most important way to generate wealth is to live within or preferably below your means. This can be done by keeping an eye on your money flow. The use of a personal budget is the simplest and quickest way of analyzing your cash flow, and understanding whether you are a spender, or a saver.
A budget is a periodical plan that helps its maker to allocate their incomes towards their expenses and fixed obligations.
Maintaining a budget is important because -
- Your budget will help you monitor and track your money flow on a month on month basis.
- You will be able to see how much of your money is spent on necessities, and how much on luxuries.
- After practicing your budget for a while, you will have greater awareness on where your money is going and you will be able to streamline your expenses to increase your investments, ultimately building more wealth.
- A budget will make it easier for you to evaluate your cash flows for the month and see how your money is flowing between your four segments.
How to Make a Budget?
Step 1: Be aware of your Net Monthly Income (post tax)- Apart from your salary, you could be receiving income from rent, dividends, interest payments, etc. Keep track of all these alternate incomes post-tax as well.
Step 2: Make note of your Expenses- The main Expenses that show up in everybody’s budgets may include:
- Grocery bills
- Spending on children’s school / college tuition fees
- Shopping and entertainment, including eating out expenses
- Electricity bill
- Travelling / fuel expense
- Telephone and cell phone bills
- Medical expense
- Miscellaneous expenses like society charges (if you own a home), etc..
Step 3: Keep track of your Liabilities- The main Liabilities that people can have are:
- Home Loan (the biggest and longest EMIs you will ever have to pay)
- Education Loans
- Car Loans
- Personal Loans
Cash outflows that go towards repayment of existing liabilities such as home and car loans, are funding the respective asset purchases. For example, EMI payments are regular, and are significant outflows from your monthly income. Be aware of the rate of interest on each of your liabilities. Stay updated on whether you can avail a better rate elsewhere, and whether you can negotiate a better tenure after sourcing your loan from another bank.
Step 4: Invest your Net Free Cash to build your wealth- The free cash you have left after your expenses are taken care of is your net free cash. This is the money that will go towards building wealth for your financial goals and accumulating assets. It is these ‘leftover’ funds, also known as your “investible surplus” that will build your wealth.
So if you find yourself in a situation where your investible surplus is low, or close to nil, you need to very quickly rectify the situation. The only way to do that is to cut back on unnecessary expenditures. Remember – it is better to first invest, and then spend out of what is left, rather than to first spend, and then invest out of what is left.
Financial Goals
To make sure that your budget is successful, you will have to set some objectives so that you can measure your performance easily. These objectives are known as 'financial goals'. Having financial goals will give your financial planning the direction it needs so that you can maintain your standards of living while saving and spending as per your needs and wants. By setting your financial goals you will be able to define your priorities, establish a direction and identify the results that you expect to achieve. When listing down your financial goals, take care to make your goals measurable, realistic and time bound.
How to Set Financial Goals?
Step 1: Identifying your goals of life- There are many things that we aim to do in our life, and most of these may require additional funds. The first step, therefore, is to understand your own goals. These may include -
- Purchase of home
- Purchase of Car
- Child’s Education
- Supporting your parents
- Child’s Marriage
- Retirement
Step 2: Classify your goals- After you have identified your goals, segregate them on the basis of - Priority (How urgent is their completion?); and Proximity (At what point of time from now, will you have to complete these goals?).
While priority of a goal can be high, medium or low, the proximity of a goal can be of three other distinct types -
- Short term (less than 3 years)
- Medium term (3 to 5 years)
- Long term (more than 5 years)
This will help you know what goals are to be met first. Knowing so can help you channelize your investments accordingly, based on the time to the goal and your risk profile.
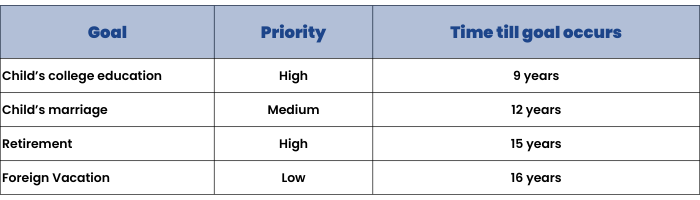
A sample table such as the one ahead will help you form an idea which goals are the most important (priority) and also see which ones are urgent (proximity). It is important to remember that this table can differ from person to person.
Step 3: Quantifying your goals- If a goal is not quantified, it becomes very difficult to select a path to achieve it. Again this can be divided into two parts, minimum and maximum.
For example, you may have a goal of funding your child’s higher education. For this you can consider two scenarios.
1. Let the first scenario be the case of your child being educated in India. For this, the fees may be ₹10 lakhs. This will be the minimum quantity of your goal.
2. Maximum amount for the goal would be sending your child abroad for further studies. For this, the fees may be ₹25 lakhs.
Now you know that the minimum you need to achieve is ₹10 lakhs in today’s terms. You can start investing accordingly.
Step 4: Plan and Invest towards your goals- Once your goals are quantified, i.e., you have a tenure, an amount and a clear idea of your goals, it is time to actually plan for these goals.
Remember, your goals should be SMART.
- Specific
- Measurable
- Attainable
- Relevant
- Time-bound
Also note that conflicting goals are a fact of everyone’s life. You must do the best that you can to resolve this difficulty by allocating your available resources in the most efficient manner possible to those goals that have the highest priority. Also, you should evaluate your investment progress regularly. If the progress towards the goal is not satisfactory, then one or more of the following options can be exercised:
- Review your investments and alter specific investment amounts / investment instruments.
- Push the goal further back, where possible.
For example, if you are planning to retire at 50, consider retiring at 55 instead, giving yourself more earning years. - Reduce the goal corpus that is required.
If you want to buy a house for ₹75 lakhs, consider starting to save for a house worth ₹60 lakhs. Setting your goals is typically not an ongoing process. You can set your goals and begin working towards them. Remember, what is an ongoing process is improving your own personal financial literacy. This is why we set financial goals - to become financially independent in the future. Review of progress towards your goals should be done typically once a year.
Basic Things To Know While Making A Financial Plan
As seen throughout the earlier units, the following things should be known and evaluated to make an efficient financial plan-
- Proper budgeting techniques
- Setting proper financial goals
- Proximity and priority of the goals
- Quantitative values of the goals
Let us understand how all these things come together to give us a foundation of our financial plan through an example.
Suppose, Mr. Amit decides to begin financial planning. He follows the guidelines given previously in this chapter, and understands his goals by tabulating them like this. Now he will start investing towards these goals based on the priorities he has evaluated and understood.
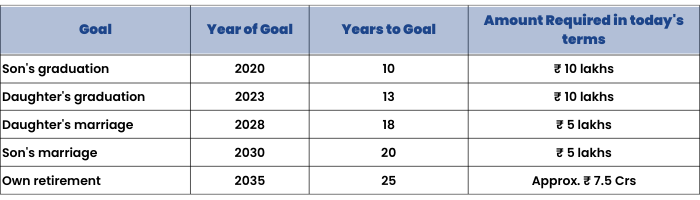
Tabulating your goals like this will help you stay clear on what you have to keep in mind while making your financial plan.
Concepts For Successful Financial Planning
Previously we have learned the basics of financial planning. But, to be successful, the first step is to build your wealth and invest wisely to maintain the right asset allocation based on your goal's time horizon. So, let us first understand the concept of asset allocation and its importance.
What is Asset Allocation?
Asset allocation is a simple concept which means allocating your investments across various asset classes. This is done so that the poor performance of any one asset class does not affect the overall performance of the entire portfolio.
There are three majorly recognized asset classes -
- Debt
- Equity
- Gold
Different asset classes are differently correlated with one another. For example, when equity does well, debt or gold may not do well, and vice versa. It is this different correlation that makes asset allocation such a critical component of financial planning.
Asset allocation differs from person and person, and it depends on the following factors -
- Your risk profile (appetite and tolerance)
- Your financial goal's time horizon
Usually, determining the right asset allocation for you is best done by your personal financial planner.
Example:
Consider two persons: Mr. Kautav and Mr. Anand.
Mr. Kaustav is a 30 year old male who is married and has no children. He wishes to plan for his retirement, and so his goal time horizon is 25 to 30 years.
Mr. Anand on the other hand is 45 years old, married and with a 10 year old child. His goals include buying a house i.e. accumulating a down payment in 5 years, sending his son to college in 8 years, and planning for his own retirement in 15 years.
Asset Allocation for Mr. Kaustav and Mr. Anand is given as follows:

Mr Kaustav already has his own house and hence his allocation to real estate is simply the value of his own home. Mr. Anand is buying a home for which he is accumulating down-payment funds. When he purchases the home, he will be buying real estate and hence adding real estate to his asset classes. He has a lower exposure to equity due to the higher number of goals, their comparative nearness in terms of years, and his higher age which reduces his risk appetite and tolerance. Mr. Kaustav on the other hand has higher exposure to equity, a riskier investment, because his only goal is retirement, and the time horizon of the goal is 25 to 30 years i.e. long term.
One should remember that asset allocation is not a one-time process. It is not static, but dynamic. As your goal draws nearer, it is important to reassess your asset allocation and withdraw from risky investments – to de-risk your goal’s portfolio. You can decide what your asset allocation should be for each of your goals. Here are some guidelines you can follow in deciding asset allocation:
- If your goal is more than 10 years away, you can invest up to 70 – 75% of your investible funds into equity, depending on your risk profile. The remainder of your investment can be put into debt (15 to 20%) and gold ETFs (around 10%).
- As your goal comes closer, for example when your goal is 6 years away, you can maintain an asset allocation of 60% in equity, 30% in debt and 10% in gold ETFs.
- When your goal is less than 3 years away, it would be wise to not expose the corpus to equity market volatility. Maintain a 100% exposure to fixed income instruments.
Risk Appetite And Risk Tolerance
The second step is to develop your own risk profile.
Your risk profile is made up of two components –
- Risk appetite
- Risk tolerance

Risk appetite simply refers to how much risk one is willing to accept. Risk tolerance indicates how much risk our finances can actually handle. The two might be very different. Let us consider an example to understand how each of them work with a hypothetical case. Mr. Arka Roy is a young man, married with a child. His risk appetite may be high. What does this mean?
This may be based on his investing tendencies. In case he has done well with equity in the past he might feel confident about it in the future as well and therefore, he might have a high appetite for risk. However, based on his financial situation, which comprises factors such as the level of emergency fund he maintains, or any loan EMIs that are chipping away at his income and so on, his risk tolerance might be very low indeed.
You should assess your own risk profile to know where you stand compared to your own risk appetite and risk tolerance. Sometimes you do everything that is necessary to provide financial safety, but situations may still arise that pushes you out of your comfort zone. There may be a financial emergency or an urgent requirement for funds.
There are two ways to deal with such a situation. They are as follows:
1. The first way to prepare for a financial emergency is to have a contingency reserve of 6 to 12 months of your annual living expenses (including EMIs if any). This can be maintained in a liquid mutual fund and partly in a savings bank account for quick access.
2. The second thing that will help in such situations is having the right kind of insurance.
Risk Profiling
Risk profiling is an exercise to determine how much risk is appropriate for an investor. A risk profile is subjective. It is insensible to assume that each person will have the ability or objectivity to determine their risk profile appropriately. As we have learned previously, Risk profiling can be carried out by understanding the different factors that can affect our risk tolerance and appetite. This is done by asking several questions as part of a structured data gathering exercise. Examples of few such questions are:
1) What is your age?
A young investor will have a higher risk taking capability than an older person due to the fact that he has more time on his side
2) How many earning members are there in the family?
If the number of earning members is high then risk taking capacity goes up but if there is only one earning member then he can have lower risk taking capacity.
3) How many dependent members are there in the family?
This can affect your expenses and therefore should be kept in mind.
4) How stable are the income streams in the family?
If the job is a permanent full-time one as compared to a freelance consultant then the person will be having a higher risk taking capacity.
5) What is the level of the investor’s current wealth, in relation to the fund requirement for their various needs?
Already if the investor has gathered substantial assets then he can take on higher risk.
6) What is the liability and loan servicing requirement of the client?
If the investor has single or multiple loan EMI running then a major portion of income gets eaten up by such liabilities leaving little surplus for investing and taking risk.
7) If the market were to fall down by 10%, how will you respond?
The investor who believes in increasing his position when the market falls is obviously comfortable with risk and losses. If a market fall were to trigger an exit from the investment with whatever can be recovered, then the investor is not a candidate for risky approaches to investment. Such questions help in understanding the psyche of the investor and accordingly asset allocation can be customized for the investor.
Things You Should Keep In Mind While Investing
After deciding the correct asset allocation it is time to start investing. However, there are a few things that should be kept in mind while investing. They are:
i. Beware of So-Called Experts!
Some people can develop a tendency to invest by listening to others, including the “so-called” experts on television, newspaper, magazines, neighbours, friends and relatives. It may happen that the stocks which these so-called experts are suggesting may be suitable for the experts themselves but not for others. This can happen because financial net worth, risk taking capacity and time plays a key role in investing.
Say a stock which looks a very poor investment in the short run could be a very good investment for the long term. Hence, the right path would be either to give your money in the expert's hand or start with your own research. All novice investors may face gains or losses initially.However, with experience,they can build their own strategies and can soon develop the acumen to make their own informed investment decisions.
ii. Regular and Disciplined Investing is Important!
The most convenient way to accumulate wealth is by investing regularly and in a disciplined manner. This can be done with any of the asset classes mentioned previously. For example, when investing in the debt market, you can opt for a recurring deposit, or while investing in equity stocks, you can choose an SIP (systematic investment plan).
The asset class that grows your wealth the most over a long period of time is equity. Very often while investing, investors try to get the perfect entry and exit point of the market. This is known as timing the market, which is considered to be very difficult, even if not impossible. Instead of timing the market, try to let your investments spend time in the market.
Time Value Of Money
In this section, we will study the concept of ‘Time Value of Money,’ which is an essential component of financial planning.
Suppose, You have won ₹10 lakhs in a lottery, and suppose you were given two options to redeem the money you’ve won.
1. Would you take the ₹10 lakhs as a lump sum in one shot immediately? Or
2. Would you prefer to receive it in equal yearly installments of 1 lakh over the next 10 years?
If you are like most people, you will have taken the money immediately. This is the right decision.
This is because of the concept of the Time Value of Money (TVM) which works on the power of compounding.
FV = PV x (1+R)^ n
Where,
FV: Future Value
PV: Present Value
R: rate of return
N: Number of time periods for which the money is invested
As per the concept of Time Value of Money,
Money that is available today is worth more than the same amount of money available at a later date, because you can invest it and earn a return / interest on it.
So, for example, if you had ₹10 lakhs available today, and you invested it into a 1 year Bank Fixed Deposit offering 7.50% in compounding mode, then in 1 year your money would be worth ₹10.77 lakhs.
The money you save and invest is the Present Value in your equation. R is the available market rate of interest and this factor is usually not in our control. Available investments offer certain approximate rates of return, and what you can do is choose your investment instrument carefully. The only factor in your control is your N, the time horizon. You can increase your investing time horizon by investing early on. The earlier you start investing, the higher will be your N, and the greater will be your money’s Future Value.
Let us consider an example to understand the concept better.
There are two friends – Anirban and Soumen.
Anirban started investing at the age of 20. Every year he invests ₹1000 into an equity mutual fund. He stops investing after 20 years.
Soumen started investing at the age of 30. Every year he invests ₹3,000 into an equity mutual fund. He also stops investing after 20 years.
Assuming they both earn the same rate of return on their investment (i.e. 15% p.a.), who do you think will accumulate more wealth by their age of 60?
The answer is Anirban. His investment of 1,000 per year for 20 years grows to ₹16.76 lakhs by the age of 60. Soumen’s investment of ₹3,000 per year for 20 years grows to ₹12.43 lakhs by the age of 60. Therefore, by beginning early, Anirban has given his investment the gift of time.
Increasing your time horizon is the best thing you can do to amass more wealth.
This brings us to the Power of Compounding – something Einstein referred to as the Eighth Wonder of The World – with good reason. You know now that the higher interest you can earn and the longer time horizon you can invest for, the larger will be your Future Value of money.
Let us take up another example to understand this.
Assume that you invest ₹1,00,000. When you will compare different instruments at different rates of return (R) across different time horizon (N), you might find results like these-

The above table indicates that for the longer N, equity is a better investment than a fixed income instrument. It is not prudent to let your wealth lie in a low-return instrument when your investment horizon is long. Also, over small time periods, the difference due to higher rates of return is not very huge.It is over longer time periods that the impact is very significant.
We will discuss more on the concept of Power of Compounding in the next unit.
Power of Compounding
For many the idea of accumulating huge sums of money seems like a daunting task. In fact often this is used as an excuse for not planning at all and leaving finances to chance. Rest assured, if you refuse to make a plan and adhere to it, there's a high degree of probability that you will never achieve your financial goals.
Another misconception is that you need higher savings/investments to achieve your financial goals. Whether you achieve your financial goals or not is more often a factor of your saving and investment habits. A combination of correct investment advice, proper investments and sufficient time can help you achieve all your goals.
Another reason why it is important to start early is because of the effect of compounding on our money.
Let us understand it with an example.
Shahrukh and Abhishek are friends who share their birthdays as well; both are building a corpus for their future needs.
Shahrukh starts saving ₹10,000 each year at the age of 30 years; on the other hand Abhishek starts his savings at the age of 40 (i.e. 10 years after his friend started his savings). However to make up for the lost time, he invests twice the amount i.e. ₹20,000 per year. Both of them earn the same returns on their savings i.e. 8% per annum.
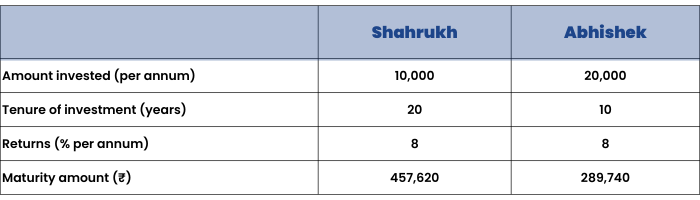
At the age of 50 years, their investment kitties would be ₹289,740 for Abhishek and a whooping ₹457,620 for Shahrukh. Despite investing a higher sum, Abhishek’s investments failed to match those of Shahrukh. The secret lies in the power of compounding.
When it comes to investments, time is money! The key lesson to be learned is to start early and give your investments sufficient time to grow.
Inflation Affecting Investment
In the early units of our module, we have discussed how inflation makes everything costlier with passing the time. Hence we need to invest our funds in high yielding assets to counter this evil. So, in this section, we will discuss how inflation affects our investments.
Purchasing power is the quantity of goods or services that one unit of money can buy. For example, ₹100 can purchase much less today than it could purchase say 20 years ago. If your income level stays the same, but the prices of goods or services increase, then it essentially means that the purchasing power of your income has reduced. This increase in the price level with the simultaneous fall in our purchasing power is called Inflation.
Inflation is one of the most important factors to account for when you are making your financial plan.
Let us understand how it affects our investments through a case study-
You are going to retire 20 years from now. Let’s see what happens if you invest in instruments that don’t match or beat inflation. Let’s take a figure of ₹10,000. Assume an inflation rate of 10% and take a time period of 20 years. As per the formula given for calculating the future value of money in the previous section, in 20 years, you will need a figure of ₹67,275 to have the same purchasing power as your ₹10,000 today.
You have 3 choices of where to invest your ₹10,000 today –
- A bank savings account
- A debt mutual fund
- An equity mutual fund
Let’s see how each one fares against an inflation rate of 10%.
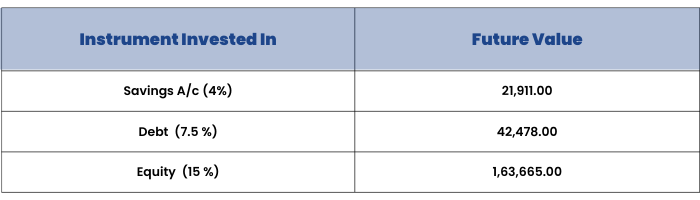
The amount you require to simply keep the purchasing power of your money constant is ₹67,275, but the inflation at 10% has eaten into the value of your money so much that over 20 years, even investing in a debt product at 7.50% p.a. is not enough.
You need to earn at least 10% every year to just match inflation and keep the purchasing power of your money intact.
In the table above, it is only equity that’s earning 15% p.a., that matches and beats inflation.
You can also match and beat inflation by investing into a mix of equity and debt instruments i.e., diversifying your investments across different asset classes, which is why asset allocation is an important concept to understand.
Now that you know are aware of the basic idea of investing and why is it important? It is time to create a full-proof plan to achieve our financial goals at different stages in our life. So, from the next section onwards we will dig deep into world financial planning.
How To Plan For The Different Stages Of Life?
Planning is required at different stages of our life, especially financial planning. So, let us begin this section by answering the below question:
Why Should We Plan?
Have you heard of this thumb rule for investing in equity?
It states that you should have (100 - Your Age) % of your net wealth in equity. So if you are 40, you should have 60% of your net wealth in equity.
But is this necessarily correct?
Your equity exposure depends on the proximity to your goals, and it is very doubtful that anybody has only one financial goal in their lives. Therefore, a single equity percentage based on your age cannot apply.
Two generations ago, life was comparatively much simpler financially. You would go to school, maybe to college, get married in your 20s, have children by your 30s, work in one company for almost your entire working life, buy a home on retirement, and retire peacefully by 60.
Things are different now. Creating a successful and powerful plan for your financial life in today’s times has very little to do with your age and a lot to do with major life stages / events when you make the plan.
Therefore, for maintaining our financial well-being throughout our life, we need each stage of our life to be carefully planned out from a financial point of view.
Let us discuss the planning for each of the three major stages of our lives-
- Our first job
- Marriage and settling down
- Financial freedom
We will elaborate our discussion on each of the three stages of life in the subsequent sections.
Stage 1: Our First Job
At this stage, you have just graduated from college, and therefore, your prime goal should be to learn how to manage your new cash flows.
Some of the features of this stage include -
- The lack of any financial dependents on your income;
- A low bank balance;
- Low tax incidences; and
- The limiting of financial goals to yourself and your family members.
Suppose, you’ve graduated and just got your first real job. A critical concern at this time is managing your cash flow.
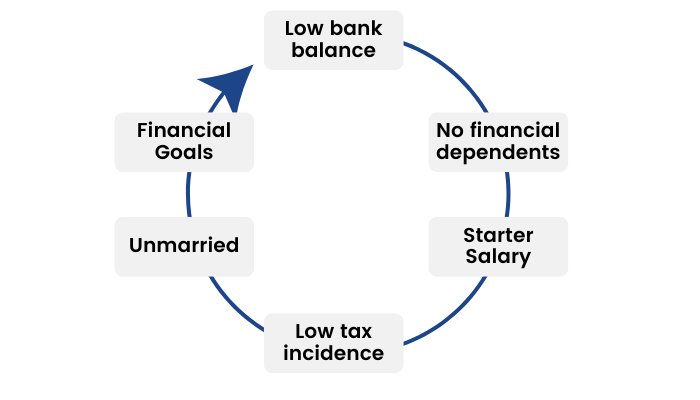
Here are some of the financial processes you should start focusing on to ensure your financial well-being-
I. Start saving
Although you might feel like you don’t have the money, even saving 10% of your income per month is enough to start planning for your retirement.
If you’re 23 years old and in your first year of working you manage to save and invest ₹24,000 (₹2000 a month for 12 months), then at a growth rate of 15% per annum this ₹24000 will grow to ₹36.75 lakh by your age of 60.
II. Insurance
You, most likely, have no financial dependents at this time so you might not need life insurance, but you should definitely opt for health insurance.
This has dual benefits.
- Your health is insured; and
- You can claim a tax deduction of the premium paid, under Section 80D.
III. Tax Efficient Investments
If your salary brings you into the 5% or 20% tax bracket, the first thing you should do is avail of Section 80C deductions. You can do this by-
Investing into an ELSS fund (equity exposure); and
Making your PPF / EPF account (debt exposure), etc..
The limit of these deductions is ₹1.50 lakh under Section 80C.
IV. Contingency Fund
Start building up a contingency fund for use only in case of emergencies.
Typically this should be the equivalent of 6 to 12 months of your monthly expenses - depending on your personal risk appetite.
You can set this aside into a liquid mutual fund to earn a better rate of return than your savings bank account.
It is important to remember that the aim of this fund is to enable liquidity of money and not just high returns.
Stage 2: Marriage And Settling Down
In this stage, you will find yourself with a higher salary and you will probably be looking to settle down and get married.
Some main features of this stage are-
- You might be married, with or without children.
- You may have planned to purchase real estate
- Personal goals would include progressing in your career, caring for your family (parents, spouse, children if any), enhancing lifestyle (vacations, car, other regular lifestyle expenses)
- List of financial goals might include planning for children’s education & marriage, house purchase, own retirement, providing for parents, purchasing a property as an investment to yield rental income
- You may or may not have adequate life insurance and health insurance for you and your spouse and children.
- You will feel the need to grow wealth, and build a better contingency reserve.
Let us look at some of the important financial concepts we should prioritize in this stage.
I. Getting Proper Insurance for You and Your Family
It is very important to first prioritize your own life insurance requirement.
Also, it is advised that you buy life insurance in the form of a simple term plan and not any other type of product.
The premium for a term plan of this kind is the lowest and the cover you will get for this premium is the highest.
This is the best way to protect your family in case of your untimely demise, especially if you also have any liabilities like a home loan / car loan.
A financial planner can help you to do an exact assessment of your insurance requirements and suggest the most suitable policy from the universe of hundreds of policies.
Also, for health insurance - take a family floater that covers your dependents.
Ensure that you have sufficient cover for each member of the family, considering that medical costs can be quite high these days.
II. Building a Contingency Fund
It is important for you to assess your contingency (emergency) reserve.
This reserve should contain 6 to 24 months of your monthly expenses, including the charges of your EMIs if any.
You can hold this fund in a liquid mutual fund scheme. This should be used only in case of a financial emergency, which can occur at any time.
Please remember to not use this fund for big ticket expenses like contributing to a new car or a vacation. You never know when an emergency might occur and how much cash you will need.
An economy is often hit with periods of recession, following which you will need to make sure that you have enough funds to pull through.
It is at times like these that you will require a good emergency fund, and that is why it is essential to have one.
III. Achieving the Right Asset Allocation
When you approach a financial planner, the first thing they will want to focus on is your asset allocation.
Asset allocation implies the decision of how much to invest into each of the asset classes – equity, debt, gold and cash, and in which specific instrument.
The objective of developing an asset allocation suited to you, is to ensure that you achieve all your life goals like purchasing property, your children’s education and marriages, your own retirement, family vacations and so on.
For this, your financial planner will take into account -
- Your risk appetite and tolerance;
- Your cash inflows and outflows;
- Your life goals and their priorities; and
- Your existing assets and liabilities.
Your planner will also ensure that as your goals approach, your goal corpus exposure is shifted from equity (unsafe, high risk) to debt (safe, low or no risk) instruments. This protects the corpus that you have built.
Therefore, your equity exposure depends on the proximity to the goal and will be different for each goal that you have.
Follow your plan and remember to invest regularly into the markets, through ups and downs. Staying in the market is the key to successful long term investing.
IV. Saving Enough Money to Buy a House
It is next to impossible to fund our own house with our own funds. Therefore, taking a home loan is usually considered essential to buy a house.
Home loans are not a cheap affair. It is important to save money to prep for the debt obligations, and following the tips given ahead can help you plan for this loan efficiently-
1. Don’t let credit card debt suck you dry
If you have a large amount of debt, then there will be no point in trying to save money as the interest you’ll be paying on your loans will far outweigh any return you will see on any savings.
Therefore, it is important to get rid of your accumulated debt first.
Also, before you take a home loan, you should put yourself in a position where you do not have any other debt to service.
Not only will that free up cash to service your loan but you will be able to take a higher loan simply because you are not bogged down by other such payments.
So the first step is to clear your personal loans and credit card debt.
2. Start saving with your very next paycheck
You can start investing in an equity fund.
You can start a systematic investment plan (SIP) where a small amount gets channelized every month towards a mutual fund of your choice.
If you do not have a long way to go, opt for debt mutual funds and select that type of debt fund which matches your time horizon and risk appetite.
3. Stop the outflow of expenses
Curb your expenses and you will be surprised at how the small savings add up.
You can start by eating at home sometimes instead of eating out multiple times a month. Reduce your eating-out budget and you will see what a big saver that is. Not to mention, home-cooked food is much healthier.
You can choose to cut down on cigarettes and alcohol too. Not only will you be healthier but even richer.
Cancel unnecessary magazine subscriptions or gym memberships if you aren’t using them. All these small moves will impact your bank balance positively.
4. Act on a definite plan
Do you have an idea how much the house is going to cost you?
For instance, if you plan to buy a home that costs around ₹50 lakh, then you will have to ensure that you have ₹10 lakh as a down payment.
Therefore, it is better to work with definite figures or else your savings may wither below the actual amount that you need.
Also, work with a time frame. Do you need that amount within a year or within five years? Once you determine that, the actual investment avenue can be determined.
V. Making a Will
In this stage, with your plans to make a family, or considering that you might already have a family, it is prudent to have a will in place.
In case of your untimely demise, your will ensures the transfer of your wealth as per your wishes mentioned in the document, and it will ensure that your beneficiaries get access to your assets without spending too much time and money.
Also, without a will, your beneficiaries would have to run from pillar to post to prove their legitimacy and thus spending lots of time along with money in case there is no Will.
With a will, beneficiaries can get these assets either tax-free or they can pay tax at a lower rate than they would have paid in case of getting these assets without a will.
Any person who is above the age of 18 is eligible to make a will.
They should be of sound mind i.e., capable of understanding their actions and should be free of any influence at the time of writing the Will.
There is no need to wait to create lots of assets/wealth till you turn old (60 – 65 years of age).
This is because, many times, people in their old age suffer from physical and mental illnesses. Sometimes they lose their capability to understand their priorities, which can prevent a person from making a proper will.
A will can be made offline or online through a lawyer or by using websites providing such services, respectively. It is not necessary to register a will but it is preferable to increase its legal power.
Stage 3: Financial Freedom
This stage begins after you’ve settled in and started a family.
After your children begin their careers like you did, you will contemplate retirement as well, or you might have retired already, depending on your age and preferences.
The features of this stage include -
- The fall in the number of dependents as your children will become financially independent;
- You will have more free time to spend with your family and on your hobbies;
- If you retire, you will have no salary or business income. Your income will come by way of dividends and interest from your investments;
- Inflation is a concern because it might reduce the money value of your assets; and
- You might have to deal with health issues as your age increases.
The following points should be kept in mind while prepping for this stage -
I. Know Where You Stand Financially
At this stage in your life, you would have retired from your job or from the business and it is expected that you would have built up a portfolio of investments that will tide you over your golden years.
If this has not yet happened, the other option is to reduce your lifestyle expense to a level that is sustainable.
If your lifestyle expenses are not within your means, you might find that you outlive your wealth, and that is not a situation you should be in.
If you choose to get a financial planner, they can crunch the necessary numbers to see what level of expense is safely sustainable and can suggest various alternatives to live within your means if the level of wealth required is higher than the level of wealth available.
II. A Contingency Fund
At this age, apart from the contingency fund you’ve been maintaining, you might want to have a separate contingency fund set aside for only health emergencies.
This can be made to hold a few lakh rupees, since medical treatments can be expensive.
This fund can also be used to supplement your health insurance in times of medical emergencies.
The medical contingency fund should cover and above your contingency fund for other emergencies.
III. Asset Allocation
At this time, your invested assets should not be at any risk, so equity exposure should be kept to an absolute minimum, or preferably brought down to 0.
This again depends on the level of wealth available. If you have built the required corpus, you need not take on any risk whatsoever.
If not, and your expenses are already brought down to the basic requirements, you might need to consider opting for a reverse mortgage on your home, and/or taking on minimal equity exposure, such as by way of a Monthly Income Plan or a Balanced Fund.
IV. Insurance
There are not many options for health insurance for senior citizens. Your best option is to continue with an existing health insurance policy, provided it is a useful one for you.
If the policy is not suitable to your specific health requirements, you can consider switching health insurance providers, but this can be an expensive proposition.
Therefore, one should be careful while assessing the available policies carefully.
A mistake most people make is they don’t read the insurance policy document and rely on their agent to tell them anything relevant. Please refrain from doing this.
It is your own responsibility to read the necessary documents and educate yourself on the investments or products you opt in to.
If you feel confused, your financial planner can help you assess various policies and then suggest the best one for you.
V. Making Tax Efficient Investments
The investments on which deductions are available are a great way to start building your wealth if you haven’t done so before reaching this stage.
If your income is above the tax free limit allowed to senior citizens (currently Rs. 3 lakhs per annum), the following options can be utilized:
- PPF (Public Provident Fund)
The interest rate on PPF for the quarter ending June 30, 2022 is 7.1 % per annum (compounded yearly).
Keep in mind that there is a lock-in period after which you can withdraw within certain limits. This is suitable for your longer term investments.
- Fixed Maturity Plans (FMP)
FMPs usually range for a duration of more than 3 years.
The expected rates of return are reasonably high but they are riskier than bank fixed deposits.
You can avail indexation benefits on these funds as well.
- Senior Citizen Savings Scheme (SCSS)
This gets you a tax deduction on the invested amount, however interest earned (7.4% p.a., paid out quarterly) is completely taxable. This option is good for safe, guaranteed, regular income
- Bank deposits
A high yielding 5 year Bank Fixed Deposit will give you an additional 0.25% or 0.50% as a senior citizen, and the invested amount is tax deductible.
Here, the interest earned will be fully taxable in your hands.
At the age of 60, achieving safe and regular income is a major goal. This can be done via the investments given above.
Loans
To fulfill some of our needs and wants, we often take loans. However, successful financial planning involves managing our debts effectively and efficiently. So, in this section, let us understand the basics of loans and the different types of loans available in the market.
What is a Loan?
Simply put, a loan is an arrangement that we make with the borrower. In this, the borrower agrees to lend us money, and in return, we agree to pay back the same money, but with a premium charged on it. This premium is known as the interest, and it is the rate of interest that most importantly affects our loan-taking decisions.
What are the Types of Loans Available in the Market?
When we take a loan from the bank, we often have to provide some sort of security to ensure that the bank can minimize its loss if we fail to repay the money.
It is on this basis that we have the most basic categorization of loans. Loans can either be secured or unsecured.
A Secured Loan is one where you, the borrower, pledge some asset of yours as collateral to the loan. Examples include car and home loans.
An Unsecured Loan refers to any kind of loan that is not attached by a lien on any of your specific assets. Examples include credit card debt & personal loans.
Mostly, loans are differentiated on the purpose of which they’re being taken for. Some of the popular categories of loans here include-
1. Auto Loans
These loans are picked up to purchase a vehicle. Since the lender retains the title of the vehicle till the loan is repaid, it is considered to be a secured loan. Some of the popular banks of the country offer the following rates as on the month of August 2019-

2. Personal Loans
A personal loan can be taken for any purpose but is usually taken to fulfill major household expenses like medical and wedding expenses. Following are the interest rates offered by some of the major banks in the country-
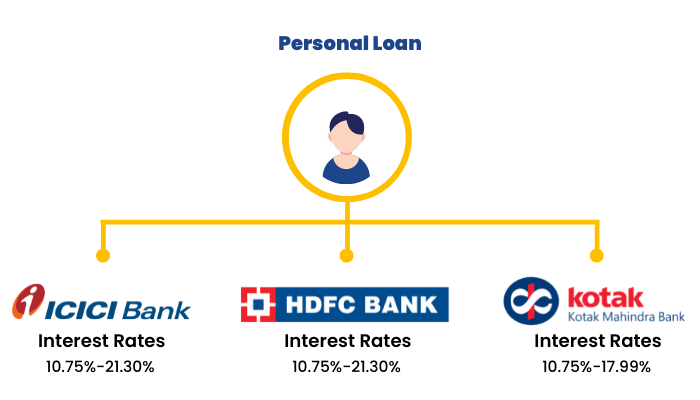
3. Home Loans
A home loan is taken for the purpose of buying a house, or land for constructing a house, among other purposes. These loans are usually secured.
Following are the interest rates available on home loans in popular banks-
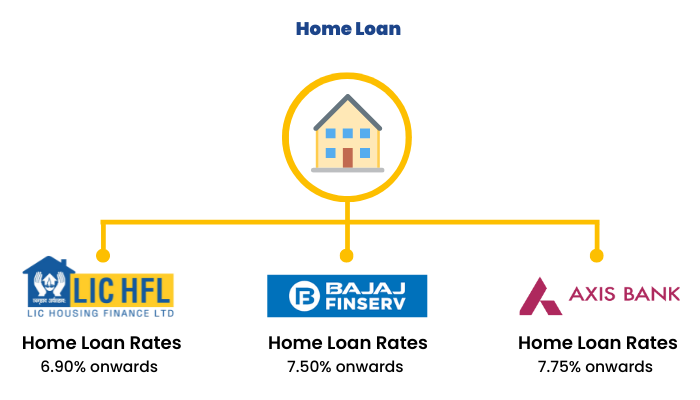
4. Education Loans
These loans are usually taken to pay off the tuition fees of a college course.
These loans take care of the following expenses-
- Fees of the institution including examination and library fees;
- Travel expenses for abroad;
- Cost of books and equipment required;
- Any insurance for the student, if applicable; and
- v. Any additional expenses such as tours, thesis, project work, etc.
These loans are usually unsecured. Following are the rates available for these loans in the country -
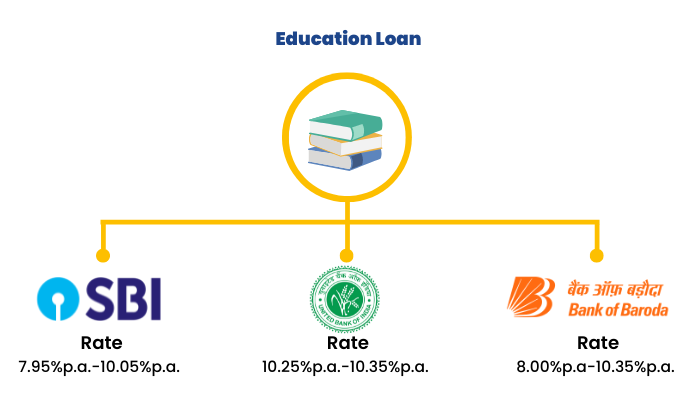
Source - https://www.bankbazaar.com/education-loan-interest-rate.html
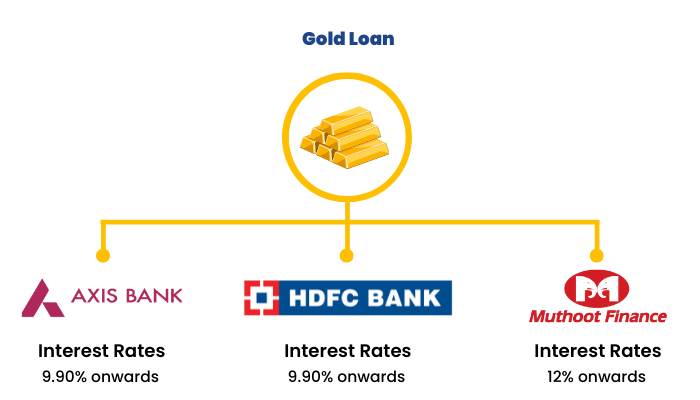
5. Gold Loans
This is a secured loan where the loan money is provided in exchange for gold as collateral. Following are the interest rates offered by various popular banks for this purpose:
After going through these options, you will face the question of how to ensure that you don’t over-borrow and put a strain on your finances. A simple way to check whether you are over-leveraged or not is to find out your Debt to Income Ratio.
Formula = Sum of monthly outflows / EMIs / total fixed monthly income
Ideally, this ratio should not be more than 30%, else you might be exerting strain on your income to service your debt.
How can we build our wealth using loans?
Taking a loan can be a great way to build your wealth provided you know how to use it smartly within the laws of land.
For example, a home loan or a car loan can help you achieve your financial goals of buying a home or a car (by making payments over a period of time) without having to wait and save enough to make an outright purchase by paying a lump sum amount.
In case of a home loan, there are tax benefits both on principal repayment and interest payment. Since you are not going to pay in lump sum but via EMIs so it provides a way to build an appreciating asset like a residential flat. Therefore, if you make informed borrowing decisions, you will be able to generate assets with the help of loan funds as well. Also, when one takes loans, they don’t have to pay the amount back in lump sum. We are liable to pay the loan amount in EMIs, as discussed ahead.
Different Types Of Interest Rates
Interest is the price we pay to borrow money. As discussed earlier, the rate of interest is different for different loans. But broadly based on the type of interest rate charged, a loan can be of two types-
Fixed interest rate loans charge a steady interest rate throughout the tenure of the loan. The EMI therefore remains constant during the tenure of the loan. It is generally better to opt for a fixed rate only when the prevailing interest rates have reached rock bottom levels and if interest rates are expected to rise.
Floating interest rate loans charge interest that moves with the market lending rates and thus, is prone to fluctuations. The EMI would increase or decrease depending on the interest rate movement. It is generally better to opt for a floating rate loan only when the prevailing interest rate levels are expected to fall further.
EMI
In earlier units, while discussing different types of loans, we have come across the term EMI several times. Let us now understand the concept of EMI and how they are calculated.
What is an EMI?
The Equated Monthly Installment, or the EMI, is the amount of money paid by borrowers, each calendar month, to the lender, for clearing their outstanding loan.Generally, EMI payments are made every month on a fixed date for the entire tenure of the loan.
How is an EMI Paid?
When the loan starts, the interest component is very large, and the principal component is very small.
Every month, the interest component becomes lower than the previous month, and the principal component becomes higher than the previous month. As the loan matures, and as the principal gets paid, the outstanding loan amount reduces.The EMI amount is a fixed amount each month, except in the following cases:
- When the borrower prepays a part of the loan, the lump-sum amount prepaid gets adjusted against the outstanding principal balance,thereby reducing the EMI. The borrower in this case also has an option of maintaining the EMI while increasing the loan tenure.
- If the borrower has opted for a floating rate loan, fluctuations in home loan interest rates during the loan tenure will alter the EMI.

How is an EMI calculated?
The basic components of an EMI are the principal and the interest payment.However, different lenders may use different computation methods for the EMI. Some of these include-
- Annual reducing method - Though the EMI is paid monthly, the adjustment of principal and interest is made at the end of the year. The main drawback of this method is that borrowers continue to pay interest on a portion of the principal that has already been paid back to the lender.
- Monthly reducing loans - The better and most common method, it reduces the principal with every EMI paid, each month. The interest is calculated on the outstanding balance.
- Daily reducing loans - Reduces the principal every day, with daily loan payments. Interest is charged on the outstanding balance. Practically, of course, such daily payments are not feasible, hence this method isn’t popular.
Which Factors Can Affect Your EMI?
The following factors can affect the amount of your EMI payments-
1. Principal amount – The actual amount borrowed from the lender.
2. Rate of interest – The rate at which the amount is being borrowed from the lender. Higher the interest rate, higher will be the EMI amount.
3. Tenure of the loan – This is the duration for which the loan has been taken. With a longer tenure, borrowers intend to repay their obligation slower; hence the EMI would be low and vice versa.
4. Method of computation – How the EMI is computed depends upon the method used by the home loan provider, either daily, monthly or on an annual reducing basis.
Plan Your EMIs
Properly planning your EMIs is an important step towards successful financial planning. How? So, to explain, let us take an example of a home loan.
A home loan is a long term decision for borrowers. It therefore pays to keep in mind the following points:
1. Consider the various personal milestones before committing to any lender. - Expenditures on an additional family member, children, etc. should be factored in when deciding on your EMI.
2. Financial institutions offer various schemes to attract potential borrowers. - One must read the fine print of the documentation carefully to understand the effective rate of interest and other terms and conditions of the loan.
3. One should avoid stretching beyond one’s capacity to pay. - Factor in for interest rate fluctuations and other debt obligations, when arriving at the EMI.
4. With uncertainties in life and job, it may be better to repay one’s debt sooner. - Consider the prepayment option if possible, to reduce the debt obligation.
5. Avoid EMI defaults, by keeping in mind the date at which the EMI is to be paid. -Maintain an adequate balance in your account on the relevant date so that the EMI payment is made successfully.
Mathematically, EMI’s are computed using the formula mentioned below.
EMI = (Loan Amount x Interest) x (1 + Interest) ^n/ {[(1 + Interest) ^n] – 1}
Interest = (% rate)/12
n = Loan period in months
Example calculate the EMI for a loan of ₹10,00,000/- at 9% p.a. interest rate and loan tenure of 15 years.

This EMI of ₹10,142.67 is a combination of both the interest and principal portion of the loan, to be paid every month.
Rising Interest Rates - What Should You Do?
Rising and falling interest rates are expected in every economy. However, it is obvious that it does not affect us if we have taken a fixed interest rate loan. But suppose, if we have taken a floating interest rate loan and the interest rates are on the rise, it means our cost of borrowing will increase. In this case, we can choose to exercise multiple options instead of paying a higher interest amount.
The options are as follows-
a. Increasing the loan tenure and keeping the EMI constant
When interest rates rise, a sudden rise in EMI could be quite a pinch, especially for -
- Individuals in tight financial conditions;
- Individuals with more than one debt; and
- Individuals nearing retirement.
At such times, keeping the EMI constant and increasing the loan tenure works out as an ideal option. Lenders accommodate the interest rate increase in the increased loan tenure and retain the monthly outflow at the same level. However, keep in mind that by doing so in the long run, you end up paying more interest for your loan. Some lenders may not permit an increase in loan tenure beyond a specific term, especially for those nearing retirement. So, check with your lender on the possible way out.
b. Increasing the EMI, with the same loan tenure
For those who can afford it, go for a higher EMI while maintaining the same loan tenure. This is because, by increasing the EMI and retaining the same loan tenure, though the monthly outflow will become higher, the total cost of the loan will work out to be much lesser. The increase in EMI must be within your financial capacity to make payments every month.
c. Loan Prepayment
For many borrowers, loan prepayment could be the last option in times of high interest rates, as it primarily depends upon the liquidity position. When going in for a prepayment, remember to check on the prepayment charges the lender would quote. Consider prepayment only if the cost of prepaying the loan works out to be much lesser than the rise in interest rate.
Loans could also be part prepaid. By doing so, the loan principal value comes down, thus reducing the total interest amount you’ll pay.
The EMI would reduce, or at least, the same EMI would remain even after an interest rate increase.
Some banks may not even charge a penalty for up to a certain percentage of prepayment.
A combination of a part prepayment with a marginal EMI hike could sometimes work out as an ideal option, if funds are available to do so.
Now comes the big question - when is the best time to prepay a loan?
This question is quite relevant for home loans, as the amounts (and thus, the interest) involved is very large.
Towards the end of a loan, you are mostly paying the principal and very little of interest. Whereas towards the beginning of a loan, you are mostly paying interest, and very little in terms of repaying the principal.
Therefore, if you repay the loan towards the beginning, you would be saving a lot more on the interest than if you repay the loan towards its end.
d. Loan Refinance
Loan Refinancing means replacing your existing loan, with a new one, under fresh terms and conditions. When interest rates rise, switching over to a lender who is offering a reduced interest rate, could serve to be a good deal. At a charge, you could switch over from a fixed to a floating rate, or vice versa.
Many lenders are more than happy to attract borrowers by lowering their interest rates. However, this process does not come easy. Be ready for a lot of paperwork along with foreclosure charges, and processing fees. Do take into consideration the penalty which the previous lender would impose. In spite of the penalty, if the new lender’s interest rate works out cheaper, it is worth a consideration.

Is It Always Beneficial To Prepay Your Loan?
Previously we have discussed how prepaying loans can be an option when interest rates are on the rise. But is it always beneficial? Let's see:
There are some investors who once they have taken a loan, prefer to prepay it as soon as possible because the idea of being ‘in debt’ is not comfortable for them.
This is a personal matter and while there is no question that these investors genuinely feel uncomfortable about the loan It is not always necessary that prepaying make financial sense. The simple reason for that is the opportunity cost of your money.
For example, if you have a loan which is charging you interest at 10% p.a., and you suddenly come into some surplus funds.
You know that you can either use these funds to prepay full or part of your loan, or to invest. The first thing you should do is check the opportunity cost of these surplus funds.
Would it make more sense to prepay the 10% interest loan, and thereby save yourself from paying the 10% interest?
Or would it make more sense to invest the funds into an investment product that can generate more than 10% return - based on your risk appetite and time horizon?
If there is an investment instrument which would give you a long term rate of return that is higher than the rate of interest you are paying on your loan, it makes financial sense to invest the funds and earn the higher rate of return, than to prepay the loan (in full or in part) and save yourself the lower rate of interest.
Debt Management
It is very easy to get into debt nowadays.
Almost everybody at some point in their lives takes a significant amount of loan or some type of debt i.e. credit card debt, home loan, personal loan, car loans, or even a combination of these loans.
If you find yourself in a situation where you feel like there is too much debt to handle and you need to get out from under the debt as soon as possible, there are some simple steps that will certainly help:
i. Breathe
It might feel like this is a great burden, and perhaps it is indeed taking a toll on your finances, but worrying about it will not make it go away.
The first thing you need to do is realize that you need to take control of the situation – and the steps to do so are very simple and straightforward.
Do remember that this is not an uncommon situation, it happens to a lot of people and anybody can get out of it by taking very simple baby steps towards a solution.
ii. Do Not Increase Your Liabilities
If you find that you are already stretched, you may find that well-wishers are advising you to take another loan to pay off your existing loan.
You would simply be delaying the time when you do have to sit down and pay off the debt. Do not add to your existing liabilities by taking on more loans.
Once the existing liabilities are cleared, if you find that you need to take another loan–
- Make sure it is easily serviceable by your existing monthly income; and
- The terms (tenure, rate of interest) are suitable to you.
This should be done only after your existing liabilities have been paid off.
iii. Take Stock of Your Liabilities
Maintain a Personal Budget.
This simple and often ignored tool is an excellent resource in your battle against debt and by maintaining a good personal budget, success against debt is achievable.
Create a table which contains all details of the various loans taken, loan type, each loan’s outstanding tenure, EMI, rate of interest and outstanding amount.
If any of the loans are collateral-based/secured, you might want to clear those first.
The rule to be followed is that you should pay off the highest interest-rate-debt first.
Loan Restructuring
In this section, we will understand the concept of loan restructuring. It is somehow similar to loan refinancing that we have learned earlier in this module. So, let us begin:
Loan restructuring is the process of renegotiating the terms and conditions of the loan taken so as to make repayment of the loan easier.
This should be done when you feel that the EMI is taking too heavy a toll on your income, or when you are nearing bankruptcy.
There are two ways to restructure your loan-
First, restructure your loan for a lower Interest rate.
Talk to your lender. Explain that you have a genuine interest in repaying the debt.
Most lenders would rather restructure your loan than turn you into a ‘bad debt’ on their books and lose the money altogether.
Try to refinance in such a way that you get a lower rate of interest as well as a lower tenure. Most individuals end up getting a lower interest rate i.e. lower EMIs, but a longer tenure.
Therefore, you will be paying back the same or perhaps a higher amount in the long term.
This would be helpful if you need to ease the current strain on your cash flows by reducing your EMI.
Also remember, if you are refinancing a home loan, there are conditions and payments which need to be considered such as-
- Minimum number of EMIs paid on the existing home loan;
- Prepayment penalty by the existing home loan lender; and
- Processing fees paid to the new home loan lender.
If the new home loan is cheaper and the savings by lower EMIs are greater than the fees you may incur, then refinancing your home loan is a suitable option for you.
Second, see if a Balance Transfer is Suitable.
For credit card debt, you can opt for a balance transfer, but this has to be done carefully.
There are a number of schemes in the market where you can transfer your outstanding balance on your existing credit card to a brand new credit card with as low as a 0% interest rate.
Unfortunately, these rates are introductory only – i.e. they will last perhaps 3 to 6 months.
Thereafter, the rate charged on the new credit card will increase to the pre-stipulated rate.
Therefore, evaluate the benefits you will gain from shifting your credit card balance before actually doing it.
Planning For Our Children’s Future
One of the important steps in preparing a robust financial plan is to properly plan for your child's future. Here, we refer to the cost of children's education. Let us understand the need and importance of it.
Why Should We Plan for Our Children’s Education?
What’s the biggest financial commitment of a parent today? At least two out of three say, “It’s to meet the rising costs of their child’s education.”
In fact, we Indians so strongly believe in the adage ‘education is insurance’, that we are willing to cut down expenses on shopping and outings to save for our child’s education. However, given the low level of financial awareness in our country, it wouldn't be surprising if many of us fall short of funds. If we dig into our retirement savings (as many of us do), we will be forced to reduce our retirement corpus, and reduce our standards of living post-retirement, and we will possibly end up becoming a financial burden on our children.
In the old days, people could earn a sound interest by investing in-
- Public Provident Fund (PPF);
- Kisan Vikas Patra (KVP); or
- National Savings Certificate (NSC).
Even with minimal planning, these instruments could help parents make ends meet and save enough for their children at the same time. Today, the rate of return on these traditional products has gradually come down over the years, and not to mention, with inflation fast catching up. In fact, most financial planners might tell you that as inflation rises, the first thing to get impacted is the education sector. This is why planning for the child’s future is an important step.
In the last one decade, the cost of education - especially quality education and foreign education has moved up substantially. The cost of primary education in quality international schools is anywhere between ₹1 lakh to ₹2 lakhs p.a., not to mention, the skyrocketing costs at the graduate and PG levels. Adding to that the fact is that the child may pursue arts or medicine or commerce or engineering, which is not clear during their schooling years.
So, how much amount has to be set aside for their education needs becomes a very tricky question. Therefore, planning early for your kid’s future has become all the more relevant today if you want to give wings to their dreams.
Let’s understand how inflation increases the price of education through an example.
Let’s say an engineering degree from a leading college would cost around ₹10 lakhs (in today’s value) and an MBA degree would cost around ₹15 lakhs (in today’s value).
Let us assume an inflation rate of 6% p.a.. If your child is aged 5 years today, then, by the time she is 18 years (i.e. in 13 years’ time), the same engineering degree would cost you ₹21.3 lakhs and an MBA degree would cost around ₹32 lakhs - over 2-fold increase in 13 years!

Quite an eye-opener isn't it?
For parents who don't have time on their side, achieving an adequate education corpus can become a daunting task. In such circumstances, they may be forced to take a higher degree of risk (not attuned with their risk appetite) and in most cases, compromise on quality of education itself. If you don’t ‘inflation-adjust’ your child’s education savings, it can make a real dent to your future plans. So it is imperative that we make elaborate plans to meet it head on.
Effective Strategies To Build An Education Corpus
Previously we have learned why we should start planning early for our children's education. It is important to build a large corpus of funds that will help meet all the costs related to children's education. So, to build a large corpus, we have stated a few effective strategies that will surely help.
Following are the strategies you can use to build a corpus for your children’s corpus-
I. Ensure yourself first.
Yes, you heard us right. As a parent, you need to shield yourself before you start investing for your child.
Ensure you have adequate health and life insurance coverage, so that your family’s needs are not compromised in your absence.
In case you don’t have one, you should consider taking one immediately.
Those who have already bought insurance, ensure you are covered adequately. Less insurance is akin to no insurance.
Earlier, the trend was that a policy was taken in a child’s name, which was a simple money-back plan.
Now, parents take a term cover in their name, which would be replaced if there is any loss of income due to the untimely death of any of the earning parents.
Therefore, this has the twin benefits of investment and protection.
You may use insurance calculators on various websites to find out your insurance needs or can take professional help from a financial planner.
II. Open and maintain a separate “savings’ bank account” for your child’s investments and other short-term requirements.
With so many goals and different investments made to reach each one of them, it's easy for things to get jumbled.
Therefore, it is important to keep your child's investments in a separate account even if you are investing in the same mutual fund scheme or investment, for another goal.
This way, you won't accidentally end up using your kid's investments. Tracking your kid's corpus becomes easier by-
- Projecting the corpus required in the future; and
- Having a unique plan in place for each objective and allocate resources accordingly.
Projecting for the long-term is never accurate - your child might end up doing a course requiring less/more money than expected.
Also, its investment returns could be different from the ones assumed, or parents might not regularly invest the required investment amount every year.
Therefore, it is better to estimate and start investing adequately early on.
III. Asset Allocation
You may choose from a basket of products to build your child’s education corpus - these include both assured return schemes and market-linked instruments.
However, your risk appetite and investment objective should ideally dictate the investments made by you. You have to also consider the time horizon.
The right asset allocation will ensure that your funds enjoy the maximum compounding benefits.
Following is the list of assets (listed priority wise) one can choose from:
1. Mutual Funds;
- Equity Index funds;
- Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs);
- Equity-linked Saving Schemes (ELSS); and
- Large-cap Equity Diversified Mutual funds.
2. Shares and Stocks;
- If you are a risk taker, you may start-off by investing in blue-chip, FMCG and pharmaceutical stocks.
- In case you are new to the stock market (or you do not have exposure in this area), you are better off investing through mutual funds.
- These are better options as they will offer you better diversification and expertise.
- Whether you are an old or new investor, you should buy stocks only after thorough research.
3. Debt Investments;
- Post Office Savings Schemes; and
- Bank term deposits.
4. Other Investments; and
- Gold ETFs; and
- Real estate.
5. Insurance.
An ideal portfolio would comprise instruments from all the above categories in varying proportions - a judicious mix of debt and equity so that you have both safety and returns.
Nowadays, some fund houses offer dedicated child plans as well (children’s ULIPs and children specific mutual funds).
However, one needn’t have to buy everything that’s offered in the market in the name of children’s specific investments.
A right mix of the above products will do the job and will cost you much cheaper.
Parents are advised to read the product prospectus carefully before investing. You can even consult a financial planner who can assist you with products specific to your requirements.
For example, a ‘children specific mutual fund’ is not quite different from the normal mutual fund schemes available today. You might as well just invest in top rated equity diversified schemes and index ETFs.
Whichever scheme you invest in, a disciplined approach holds the key to financial freedom.
IV. Do consider Systematic Investment Plans (SIP).
An SIP offers a lot of advantages - the main being the ease of investment.
An SIP can be made for equity mutual funds through the ease of internet banking (ECS debit facility) and therefore, can happen smoothly every month, without feeling a pinch in your pocket.
V. Keep evaluating the performance of the various investments.
You should do so at regular intervals like a 3-year or a 5-year period to find out if they are shaping up as expected.
When the goal is a couple of years away - move the assets to safe debt instruments, so that any falls in the market/economy do not erode the gains you made so far.
The ideal way to build an adequate corpus for your child's future is to go step by step. The earlier you start the better.
A combination of correct investment advice, proper investments and sufficient time can help you achieve all your goals.
Making Your Investments
Once you shortlist investments, it's time to invest.
You could either invest in your child's name or make investments in your own name.
For those who have started late or finding it difficult to manage your child’s investments due to other obligations – do not fret.
There is the comfort of an ‘education loan’ for higher studies. Also, considering the rising cost of higher education over the years, many would find it hard to find the entire course expenses through their own resources.
Stay away from taking a personal loan towards education purposes as personal loans are typically more expensive.
Additionally, education loans are eligible for a tax deduction under Section 80E on the interest paid on loans taken for higher education for yourself, your spouse and children.
There is no limit on the amount of deduction you can claim.
The only thing to keep in mind is that the course for which the loan is taken should be a graduate or post-graduate programme in engineering, medicine or management or a post-graduate course in the pure or applied sciences.
However, banks have always maintained a lower approval ratio on education loans - so it is prudent to maintain a respectable credit history, and accumulate as much as possible through one’s own resources.
Retirement Planning
After we have completed planning for our children's future, it is time to consider planning for our own future, i.e., Retirement Planning.
What is the Need for Retirement Planning?
Did you know that from the very first day you receive money, the pocket money you received as a child, you have been an 'investor'?
Think back to the first day you received pocket money. You most likely spent it on food, toys, games, movies and other entertainment, and travel. How much of it did you save? Not much, if you were like most children in school and college. You invested in instant gratification, as do most youngsters. From this young age, your activities, your spending patterns, formed a habit. Your investment behavior started to get set. Your investor psychology began to solidify. Then you got your first job and started to mingle in the workplace. At work, you interact with your colleagues, slowly you hear about people making investments in Tax saving mutual funds, or in their PPF. Your HR talks to you about EPF so you know about that too. You glean investment facts haphazardly from your colleagues and without really verifying the data, make further investment decisions. You get married, then have children, educate your children, somewhere along the line you buy a home by taking a home loan. The expenses continue, and your saving, spending, or investing continues as it did earlier.
Your investments receive just enough of your attention for you to feel like you're doing something useful about it. With each step you take along this path, your retirement suffers. The wealth that you could have built for this crucial goal, does not get built.
Retirement is a reality that many of you may not be able to accept, but it is pertinent to realize that one day this reality will hit you and you need to be prepared.
There is no need to fret if you haven’t started on this goal yet. This section of our module can guide you on how you should approach retirement planning.
Major Expenses Of A Retired Person
A retired life means that you have to live your life with limited or no income keeping all the expenses constant. Well, that seems really difficult. That is the reason why you need to build a retirement corpus. However, there are a few factors to consider. But before we discuss all the factors, first let us discuss the major heads of expenditure post-retirement.
The following types of expenses are the ones that retired persons will have to cover with their limited funds-

Which Factors can Affect Your Retirement Corpus?
The following factors can affect your decision of how much you want to save for your retirement-
i. Standard of Living
Your retirement corpus is used to generate a monthly income for you in your retirement. So, its size is directly proportional to the monthly amount that needs to be generated. The higher your standard of living, the more you would need each month in your retirement. This means you would need a higher retirement corpus, which in turn means that you need to save more every month while you are earning. You can roughly calculate how much you would need in your retirement from your current monthly expenses. Of course, you would have to factor in inflation, and it would give you a rough idea about your needs in your retirement.
ii. Inflation
Inflation is an important factor when extrapolating today’s monthly expenses to your post-retirement expenses. For doing this, you would use the compound interest formula and the most important factor there is the expected rate of inflation between now and your retirement. A higher rate of inflation means that you would need more money to maintain the same standard of living, resulting in a higher retirement corpus – which means you would need to save and invest more every month today.
iii. Income Expected in Retirement
Of course, if you have any other income in your retirement, that would reduce the need to generate additional amounts. This can be anything, say pension or rental income from your second flat / apartment or even small earnings from your hobbies. Basically, if you have income in any form during your retirement, your retirement corpus would be lower, which means less investment needed while you are earning.
iv. Rate of Returns / Interest Rate
The rate of return comes into play at two stages – for building your retirement corpus, and for generating the monthly income from your retirement corpus. This rate of return also directly depends upon the instruments you choose for investment while saving for your retirement, and the instruments you choose to park your retirement corpus in.If the rate of return is high during your earning stage, you would need to invest less every month. This would be the case if you are investing in instruments like shares/ equities. On the other hand, if you are investing in safe avenues like bank FDs and endowment plans of life insurance companies, the amount you would need to save every month to generate the same retirement corpus would be higher. The rate of interest post-retirement is crucial in calculating the actual retirement corpus. If you would be parking the retirement funds in safe avenues generating steady income (like most people should do), the retirement corpus needed for you would be higher, resulting in higher monthly investment requirements today. But if you can invest even some portion of your retirement corpus into high yield avenues like stocks, you would need a smaller retirement corpus, thus needing lower monthly investments today.
v. Years Remaining to Retirement
This determines how long you can save and invest to build your retirement corpus. The earlier you start, the lower you have to invest every month.
vi. Life Expectancy
The retirement corpus has to provide for your entire retired life when you are not earning. Therefore, your life expectancy plays a big role in the calculation of the retirement corpus. The higher the life expectancy, the higher is the number of years for which your retirement fund needs to last and provide for you. Therefore, the higher would be the retirement corpus, and higher would be the amount you would need to set aside for your retirement. Deciding what amount you should set aside for retirement is a complex exercise, and the above mentioned factors should help you get an idea about the amount of investment needed for building your retirement. Of course, you can also take professional help from a financial planner.
Investor Traits Affecting Retirement Planning
Well, the majority of individuals understand the necessity of retirement planning. Still, many of them fail because there are a few common traits that affect retirement planning. They are:
i. Procrastination
Procrastination means delaying your initiatives/work. It is bad for your retirement because You lose out on time, value of money and power of compounding both. For example, let's look at how the cost of delay works.
Mr. A is 25 and invests ₹5,000 per month. He is investing into equity mutual funds and will likely earn about 15% per annum over the next 25 years, until he turns 50. Mr. B is 35, and invests ₹15,000 per month. He is also investing into equity mutual funds and expects the same rate of return for the remaining 15 years, until he turns 50.
Mr. A achieves a corpus of ₹1.62 crores.
Mr. B achieves a corpus of ₹1 crore.
The solution is simple. You want to be an investor as early as possible, even if the amount is small. You must save, invest, and save some more and invest some more, and in doing so, you will build up your wealth.
ii. Overconfidence and Ignorance
Don't underestimate inflation. Don't underestimate the benefit of saving taxes. Don't overestimate your ability to deal with financial goals 'later'. Don't overestimate your health, as you get older, it will get weaker. These things might seem unrelated, but they all point towards one quality - your confidence, or overconfidence, as the case may be. If you start investing, you will know how much you need to retire, and you can start planning for it right away. You will suddenly realize the importance of dealing with goals immediately, saving taxes, and also of being adequately insured.
iii. Constant Tracking and Monitoring
Once you realize that you need to invest, and you identify the right amounts, the right schemes, the right asset allocation, you will be able to begin your investments. After this, the one thing you must NOT do, is track your investments every day, or every week, or every fortnight. If you track your investments on a daily basis, your emotions will go on the same ride as the markets - up one day and down the next. Human beings aren't built to handle this kind of emotional volatility. So invest in the right schemes, for the right amounts, for a particular goal, and monitor once a quarter or once in 6 months. If markets are crashing - excellent! Buy more - it's cheaper now! Don't follow the herd - eventually it might run off a cliff.
iv. Investing Alone Instead of Doing it As a Family
No man is an island. We all have families, and our financial decisions will affect them. The best way to go about building a retirement plan is to first sit down with your spouse and figure out exactly what you're spending now - you have to consider household expense inflation, medical expenses inflation, travel expense inflation, and the kind of lifestyle you want to maintain in your retired years.
Will you do more charity work after you retire? Will you travel more? Will you both take up hobbies?
Together, you both should sit down with your financial planner and work out your retirement plan.
The habits you built as a child dealing with your money can be modified, tweaked and bettered. You can, right now, stop procrastinating, realize the cost of delay, and start planning for your retirement.
After all, who doesn't want to retire young and rich?
Myths Associated With Retirement Planning
Retirement is like a long vacation in Las Vegas. The goal is to enjoy it the fullest, but not so fully that you run out of money. - Jonathan Clements
Below are few myths associated with Retirement Planning:
i. You need a large income to be prepared for retirement.
one does not need to have a large income to be prepared for retirement; one must need to be disciplined and start saving early.
ii. Debt is a part of life.
One should have enough money to clear their last debt and have plenty more to survive on. Having debt to take care of when retired is not prudent and it is not something everyone has if they plan ahead.
iii. Assuming your kids are your retirement plan.
People keep saying, "My retirement plan is my children. This may have been the case at one point of time but does not hold true anymore, especially with nuclear families gaining popularity.
iv. Your house can finance retirement.
Treating your house as the ultimate retirement insurance is an easy trap to fall into.
This is as firstly your house is your biggest asset class and takes up over 50% of most people's net worth, and secondly shifting houses at a later age may not be the easiest adjustment to make, especially if it is to a cheaper and smaller place.
This is as in reality it's hard to eat out on your home equity.
v. I won’t live long after retirement.
This is probably one of the most common myths and it is high time people get realistic about it.
vi. I will never retire.
Yes, you will. Everybody has to.
You may want to work till you drop dead, but what if you really cannot get a job after 55? What if your health does not permit you to work?
vii. I am too young to plan for retirement.
There is no such thing as being too young to retire or plan for retirement.
The earlier one starts the better.
One should start early as possible when it comes to retirement planning. The main advantage of starting early is that you can make the most of the power of compounding, which makes a big difference.
viii. Retirement planning can wait till my loans are paid and my goals are met.
It never works like that.
Retirement planning is a part of financial planning.
While we may have many short and medium term goals to look after, it does not mean the most important long-term goal should be ignored under any circumstances.
ix. Retirement money should stay clear of equity.
This is another big mistake that many people make while planning for retirement.
Equity, while being a riskier asset class over the long run, has always provided way better returns than fixed income instruments.
Ignoring this asset class in your retirement plan is folly, as this will help you beat inflation and gain the most out of your savings.
x. My needs post retirement will be limited.
This is a myth and a completely baseless statement unless calculated by you or your financial planner.
Judging how much money one needs post retirement is never easy and one of the best ways to do it is by figuring out what expenses you will have then.
This can be done by looking at your current expenses and seeing what part of it you will need when you are retired.
The Golden Rules Of Retirement
Experts contend that retirement planning should start from the day you start earning. Sound advice indeed, but one that is seldom followed.
Finally, in this last section of our module, we will learn the golden rules of retirement planning that will surely help you retire in comfort. The following rules are:
a. Save 10% of your income for retirement
The first rule of retirement planning is also the easiest to follow. If you have a regular job, then 12% of your basic salary and an equal contribution by your employer that flows into your Provident Fund account is a good way to build a nest egg. The best thing about this option is that you cannot avoid it. EPF rules require all employees to contribute 12% of their basic income to retirement savings, which include the Employee Provident Fund and the Family Pension Fund. It is a forced saving that becomes the default retirement plan for many individuals. The 10% rule is crucial for self-employed professionals and others who are not covered by the EPF umbrella. They can opt for mutual funds, choosing the ones that suit their risk appetite and age profile. However, you need to have the discipline to put away the given sum on a regular basis.
b. Increase investment as your income grows
It is important to maintain the retirement savings rate at 10% so that your nest egg doesn't fall short of your requirements. The icing on the cake can be periodic boosters whenever you get a windfall, such as a tax refund or a lump-sum payment in the form of, say, an annual bonus. The trick is to commit yourself to save more in the future. Whenever you get a raise, allocate half of it to savings. You might not notice the change since you will be enjoying the other half of the raise.
c. Don't dip into corpus before you retire
This might sound weird, but every time you change jobs, your retirement planning is at a grave risk. This is because you have the option to withdraw your PF balance at that time or transfer it to the account with the new employer. Your money will not reap the benefit of compounding if you dip into the corpus before retiring. Don't underestimate what this can do to your retirement savings over the long term.
For example, A person with a basic salary of ₹25,000 a month at the age of 25 can accumulate ₹1.65 crore in the PF over a period of 35 years. This is based on the assumption that his income will rise by 10% every year.
d. Withdraw 5% a year initially, then step up
One of the biggest challenges for tomorrow's retirees is to ensure that they don't outlive their savings. To ensure that you don't run out of money in your old age, you must have a drawdown plan in place. The thumb rule is not to withdraw more than 5% of the corpus in the first five years of retirement. This can be progressively increased to 10% by the time the retiree is 70. At 80, even a 20% annual drawdown rate would be considered safe.
e. 100 - Age = your allocation to stocks
An investment portfolio's performance is determined more by its asset allocation than by the returns from individual investments or market timing. How much you have when you attend your last day at work will depend on how you allocate your retirement savings between stocks, fixed income and other asset classes. Experts recommend that you should have an equity exposure of 100 minus your age. So, at 30, you should have about 70% of your portfolio in equities. After you retire, your exposure to stocks should not be more than 25-30 % of your portfolio. This isn't a hard and fast rule, though.
f. Borrow for education, save for retirement
Before you pour money into your child's plan, make sure your retirement savings target has been met. In an effort to fulfill the needs of the child, Indian parents sometimes sacrifice more than they should. Some even dip into their retirement funds to pay for the child's education. This is risky because your retirement will be entirely funded by you and won't have the cushion of defined benefits. This doesn't mean you should compromise on your child's education. It can still be done through an education loan. An education loan helps inculcate financial discipline in the child. In addition, if the child is responsible for repayment, it establishes a habit of savings from an early age.
g. Save 20 times your annual expense
This rule is different from others because it is based on how much you spend, not on how much your investments earn. Knowing your post-retirement expenses is crucial to retirement planning. Some expenses, such as those on clothing and entertainment, come down. Others, such as transportation, medicine and insurance, go up. Add up all the expenses you are likely to incur after retirement to know how much you will need per month. Then, multiply this amount by 20 to know how much should be your retirement corpus.
However, this calculation is based on a number of assumptions -
- Firstly, you should not have outstanding loans when you hang up your boots.
- Secondly, you and your spouse should have sufficient health insurance.
You are not required compulsorily to follow these rules.
These are simply different ways to help you begin your journey towards efficient retirement investment planning.
Conclusion
Finally, as the module came to end, we hope that you have learned quite an insight of financial planning and implement these strategies to attain financial freedom in your life. Do remember that planning is important but executing them in reality might be difficult. Visit this module everytime when you require assistance at any stage of your life. If you like reading this module, share it with your friends and family. Also there are a lot more interesting modules on finance at ELM School. Do read them at your convenience to learn more on finance.
Happy learning!!
Ready to master the A2Z of Finance? Start your journey to financial expertise today! Enroll now


